What Purposes Do Mosquitoes Serve in Ecosystems?
Mosquitoes play crucial roles in ecosystems primarily as pollinators and as a food source. Many species feed on nectar, aiding in the pollination of various plants. Additionally, mosquito larvae are vital to aquatic ecosystems, serving as food for fish and other wildlife. Adult mosquitoes are a key food source for birds, bats, and amphibians. Understanding their ecological roles helps appreciate their contribution to biodiversity and the balance of natural habitats.
What Is the Difference Between Hemp and Marijuana?
Hemp and marijuana are both varieties of the Cannabis sativa plant but differ in their chemical composition and uses. Hemp contains low levels of THC, the psychoactive compound, making it non-intoxicating. It's primarily cultivated for industrial purposes, including textiles, paper, and health products. Marijuana, on the other hand, has higher THC levels, leading to psychoactive effects, and is primarily grown for medicinal and recreational use. Legally, the distinction often hinges on THC content, with 0.3% as a common threshold.
Why Does
"Why does" is a question opener that invites exploration and understanding of various topics. It seeks to uncover reasons, causes, or explanations behind events, behaviors, or phenomena. This phrase can initiate inquiries ranging from scientific investigations to philosophical musings, helping to satisfy curiosity and expand knowledge. By prompting us to think critically and seek deeper insights, "why does" challenges assumptions and encourages a more profound engagement with the world around us, fostering learning and discovery.
How Do We Know What Dinosaurs Sounded Like?
Scientists infer dinosaur sounds by studying their closest living relatives, birds and crocodiles, whose vocalizations offer clues about dinosaur calls. Fossilized remains, such as skull structures and potential vocal organ impressions, also provide insights. Advanced technology like CT scans helps reconstruct possible sound-producing anatomy. Additionally, computer simulations and comparisons with similar modern animals allow researchers to hypothesize about the range and nature of dinosaur sounds, though definitive conclusions remain elusive due to the lack of direct evidence.
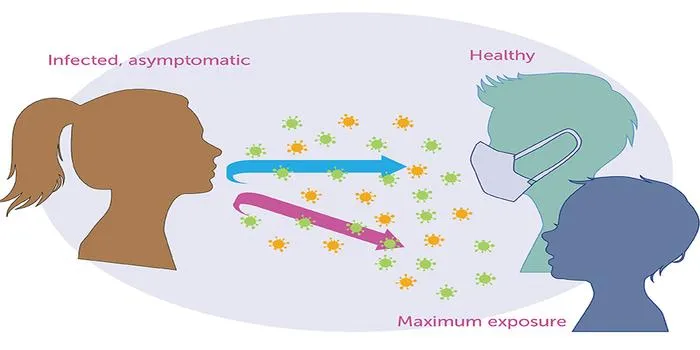
How Do Face Masks Control the Spread of Disease?
Face masks play a vital role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, especially those transmitted through respiratory droplets. When worn correctly, face masks can significantly reduce the transmission of airborne pathogens, including viruses and bacteria. By acting as a physical barrier, masks help to block respiratory droplets that are expelled when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, thereby minimizing the risk of disease transmission to others.
What’s the Difference Between Sugar in Fruit and Sugar in Sweets and Candy?
When it comes to sugar, not all types are created equal. The sugar found in fruit and the sugar in sweets and candy differ significantly in terms of their nutritional impact and health effects. The primary distinction lies in their source and the way they are processed by the body.
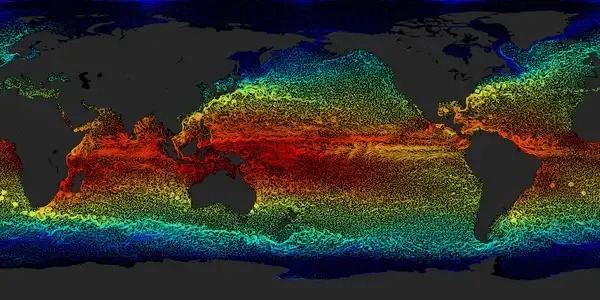
How Do Ocean Currents Affect the Biosphere?
Ocean currents play a crucial role in regulating the earth's climate, distributing heat and nutrients across the globe. They impact marine life by transporting plankton and other organisms, which form the base of the food chain. Currents also influence weather patterns by affecting atmospheric temperatures and precipitation. This dynamic movement of water supports biodiversity by creating varied habitats and helps in the dispersal of species, maintaining ecological balance within the biosphere.
Why Is Predicting the Weather So Difficult for Meteorologists?
Predicting the weather is challenging due to the Earth's complex atmosphere, which involves countless interacting variables such as temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and pressure systems. These elements are influenced by the planet's geography and external factors like solar radiation. Despite advanced technology and models, the chaotic nature of weather systems introduces uncertainty. Small changes can significantly alter outcomes, making precise long-term forecasts difficult. Additionally, data collection limitations and computational constraints further complicate accurate predictions.
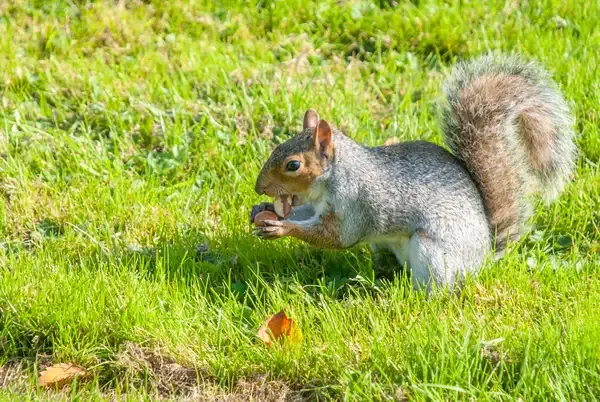
Is It True That Squirrels Forget Where They Bury About Half of Their Food?
Squirrels are known for burying nuts and seeds as a food reserve, but it's a common belief that they forget about half of these caches. While it's true that some caches remain undiscovered, research indicates that squirrels use spatial memory and landmarks to relocate their food. They have a remarkable ability to remember specific locations, though environmental factors and time can lead to some being overlooked. This behavior contributes to seed dispersal and forest regeneration, highlighting squirrels' ecological role.
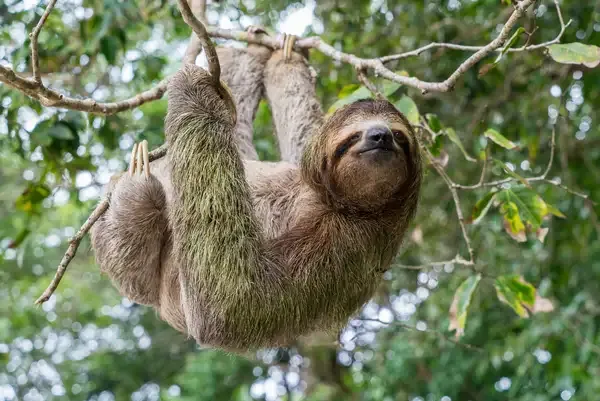
Why Are Sloths So Slow?
Sloths are slow primarily due to their low metabolic rate, which is an adaptation to their low-energy diet consisting mainly of leaves. This diet provides limited nutrition, so sloths conserve energy by moving slowly and sleeping up to 15 hours a day. Their slow movement also helps them avoid detection by predators, as they blend in with the trees in their rainforest habitats. Additionally, their muscle structure is adapted for hanging, not speed, further contributing to their leisurely pace.
Is Earth Going to Change the Direction in Which It Rotates?
Earth changing the direction of its rotation is an intriguing concept, but highly unlikely. The planet spins from west to east due to the angular momentum it gained during its formation. For Earth to reverse its rotation, an unimaginable amount of energy would be required, far beyond any natural or human-induced force. While Earth's rotation speed can vary slightly due to shifts in mass distribution, a complete reversal is not feasible with current celestial dynamics.
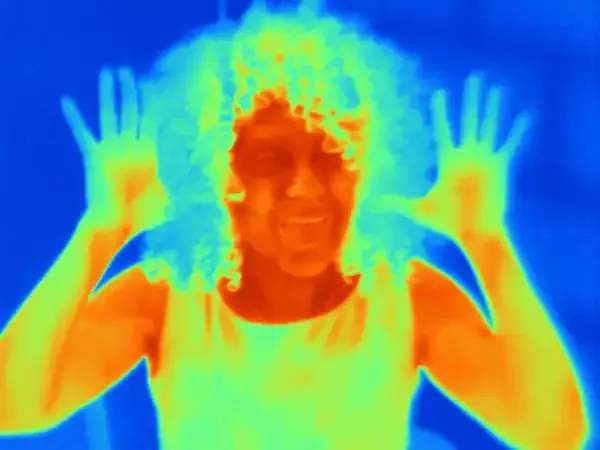
How Does the Human Body Maintain Its Temperature?
The human body maintains its temperature through a process called thermoregulation. This involves the hypothalamus, which acts as a thermostat, detecting changes in body temperature and initiating responses. When the body is too hot, it triggers sweating and vasodilation to release heat. Conversely, if the body is too cold, it induces shivering and vasoconstriction to conserve heat. These mechanisms, along with behavioral responses like seeking shade or warmth, help keep the body's temperature stable.
What Is the Difference Between Primary and Secondary Ecological Succession?
Primary ecological succession occurs in lifeless areas where there is no soil, such as on bare rock after a volcanic eruption or glacier retreat. It involves the gradual formation of soil and establishment of a biological community. Secondary ecological succession, on the other hand, takes place in areas where a disturbance has destroyed an existing community but left the soil intact, like after a forest fire or hurricane. This process is quicker, as the soil already contains the nutrients needed for plant growth.
Why Are the Babies of Mammals Cute?
Babies of mammals are often perceived as cute due to their physical features like large eyes, rounded faces, and small noses, which trigger nurturing instincts in adults. These characteristics are part of a survival strategy, as they encourage caregiving and bonding from parents and other adults. This perception of cuteness is not just limited to humans; it is a widespread phenomenon across many species, ensuring that young animals receive the care and protection they need to survive and thrive.
How Do Hurricanes Get Their Names?
Hurricanes are named to facilitate communication and avoid confusion. The World Meteorological Organization maintains a rotating list of names for each ocean basin, which are used sequentially. Names alternate between male and female and are reused every six years unless a storm is particularly deadly or costly, in which case the name is retired. This systematic naming helps meteorologists, the media, and the public to discuss storms clearly and efficiently, enhancing public safety and awareness.
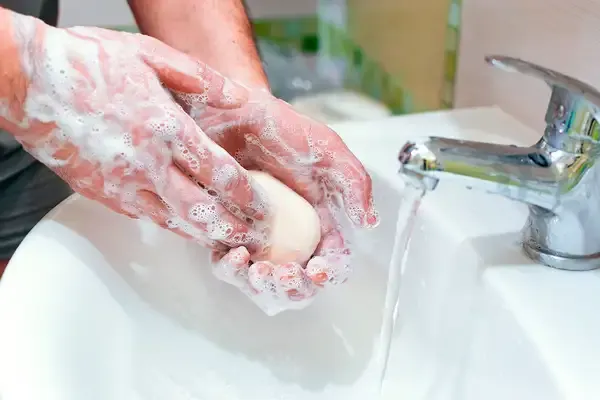
How Does Soap Work?
Soap works by breaking down and removing dirt and grease from surfaces. It is made up of molecules with hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads and hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails. When you apply soap with water, the hydrophobic tails attach to the oils and fats, while the hydrophilic heads remain in the water. This interaction creates micelles, trapping the dirt and allowing it to be rinsed away, leaving surfaces clean.
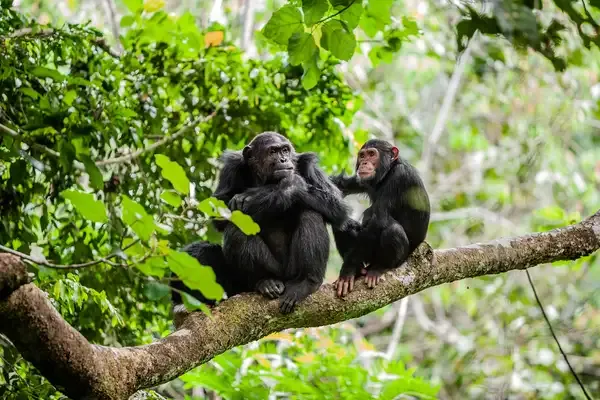
Are Chimpanzees Cannibals?
Chimpanzees are not typically considered cannibals, but instances of cannibalistic behavior have been observed in certain situations. This behavior is generally rare and often occurs under specific circumstances such as social conflicts, territorial disputes, or when resources are scarce. It is more common in certain communities or during periods of high stress. Although these acts may seem shocking, they are part of the complex social dynamics and survival strategies within chimpanzee societies.
What Causes a Volcano to Erupt?
Volcanoes erupt due to the movement of tectonic plates and the buildup of pressure from molten rock, or magma, beneath the Earth's surface. When tectonic plates shift, they create pathways for magma to rise. As the magma accumulates, gases dissolved within it expand, increasing pressure. Once the pressure exceeds the strength of the overlying rock, the magma forces its way to the surface, resulting in an eruption. Other factors like magma composition and the presence of water can also influence eruptions.
Why Is the Platypus a Mammal?
The platypus is classified as a mammal because it shares key characteristics with this group, despite its unique features. It is warm-blooded, has fur, and possesses mammary glands, which are used to nurse its young. Although it lays eggs, a trait uncommon among mammals, its physiological and genetic makeup aligns more closely with mammals than any other animal group. The platypus exemplifies the diversity within the mammalian class, highlighting evolutionary adaptations over millions of years.
A Brief History of Press Freedom
"A Brief History of Press Freedom" traces the evolution of journalistic liberty from its early roots to modern times. It highlights key milestones such as the invention of the printing press, which revolutionized information dissemination, and the establishment of legal protections like the First Amendment in the United States. The text explores the ongoing global struggle for press freedom against censorship and authoritarianism, underscoring the vital role of an independent press in fostering democracy and holding power to account.