- Home >
- Science
- > Technology
How Do Ocean Currents Affect the Biosphere?
Ocean currents play a crucial role in regulating the earth's climate, distributing heat and nutrients across the globe. They impact marine life by transporting plankton and other organisms, which form the base of the food chain. Currents also influence weather patterns by affecting atmospheric temperatures and precipitation. This dynamic movement of water supports biodiversity by creating varied habitats and helps in the dispersal of species, maintaining ecological balance within the biosphere.
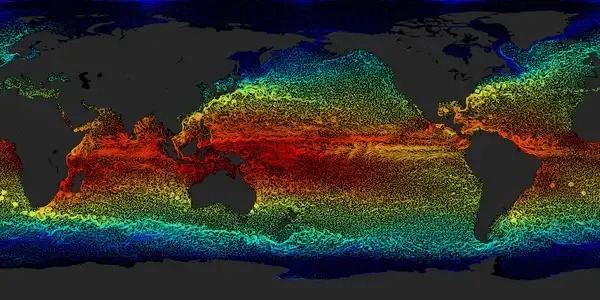
Ocean currents play a crucial role in shaping the ''biosphere'', influencing climate, weather patterns, and marine ecosystems. Understanding how these currents function and their impacts on the environment is vital for appreciating the interconnectedness of oceanic and terrestrial life. Below, we delve into the mechanisms of ocean currents and their significant effects on the ''biosphere''.
What Are Ocean Currents?
Ocean currents are large-scale movements of seawater driven by various factors, including wind, temperature differences, salinity variations, and the Earth’s rotation. These currents can be classified into two main types: surface currents, which occur in the upper 400 meters of the ocean, and deep-water currents, which flow beneath the surface. The ''global conveyor belt'', a system of deep ocean currents, plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
Impact on Climate and Weather Patterns
Ocean currents significantly influence global climate and weather systems. For example, the ''Gulf Stream'', a warm ocean current in the North Atlantic, helps moderate temperatures in Western Europe, making it warmer than other regions at similar latitudes. Conversely, cold currents like the ''California Current'' can lead to cooler coastal climates. Changes in these currents can disrupt weather patterns, leading to extreme weather events such as hurricanes or droughts.
Influence on Marine Ecosystems
Ocean currents are essential for the distribution of nutrients and organisms within marine ecosystems. They transport nutrient-rich waters from the deep ocean to the surface, promoting phytoplankton growth, which forms the base of the marine food web. The ''upwelling'' zones, where deep, nutrient-laden water rises to the surface, are among the most productive areas in the ocean, supporting diverse marine life.
Current Trends in Ocean Currents
Recent studies indicate that climate change is altering ocean currents, which could have profound effects on the ''biosphere''. For instance, melting polar ice caps are adding freshwater to the oceans, which can disrupt the salinity and density gradients that drive deep-water currents. This phenomenon may lead to changes in marine biodiversity, as species struggle to adapt to shifting habitats.
Table: Major Ocean Currents and Their Effects
| Current | Type | Location | Effect on Biosphere |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gulf Stream | Surface | North Atlantic | Warms Western Europe, influences weather patterns |
| California Current | Surface | Eastern Pacific | Cooler coastal climate, supports specific marine species |
| Antarctic Circumpolar Current | Surface | Southern Ocean | Regulates climate, influences global weather |
| North Atlantic Deep Water | Deep-water | North Atlantic | Important for global heat distribution |
Effects on Terrestrial Ecosystems
The influence of ocean currents extends beyond the marine environment; they also affect terrestrial ecosystems. For example, the ''El Niño'' phenomenon, a result of changes in ocean currents in the Pacific, can lead to significant alterations in rainfall patterns across the globe. Regions that typically experience dry conditions may see increased rainfall, impacting agriculture and terrestrial biodiversity.
Role in Carbon Sequestration
Another vital role of ocean currents in the ''biosphere'' is their contribution to carbon sequestration. The oceans act as a carbon sink, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Ocean currents facilitate the transport of this carbon to the deep sea, where it can be stored for centuries. Disruptions in these currents could affect the oceans' ability to sequester carbon, potentially exacerbating climate change.
Conclusion: Protecting the Oceans and Our Future
Understanding the effects of ocean currents on the ''biosphere'' is crucial for sustainable environmental practices. As human activities continue to impact our oceans, it is imperative to monitor these changes and implement measures to protect marine ecosystems. Preservation of ocean currents and their natural flow is essential not only for marine life but also for the health of our planet as a whole.
In summary, ocean currents are integral to the functioning of the ''biosphere'', affecting everything from climate and weather to marine and terrestrial ecosystems. By recognizing the importance of these currents, we can better appreciate our planet's complexity and the need for conservation efforts.