- Home >
- Science
- > Technology
How Do Face Masks Control the Spread of Disease?
Face masks play a vital role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, especially those transmitted through respiratory droplets. When worn correctly, face masks can significantly reduce the transmission of airborne pathogens, including viruses and bacteria. By acting as a physical barrier, masks help to block respiratory droplets that are expelled when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, thereby minimizing the risk of disease transmission to others.
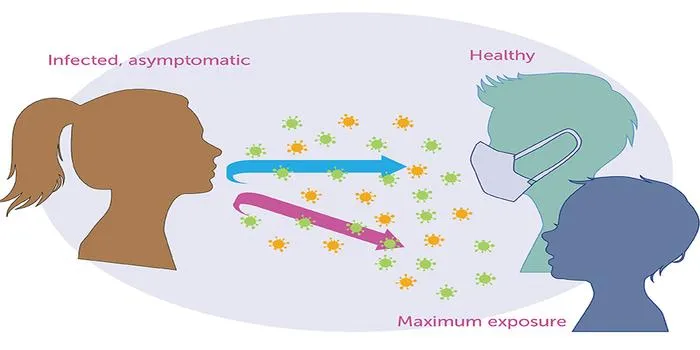
Face masks have become an essential tool in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, particularly in the context of respiratory illnesses such as COVID-19. Understanding how these simple barriers work can help individuals and communities adopt effective practices to reduce transmission rates. In this article, we will explore the mechanisms by which face masks help control disease spread and highlight their importance in public health.
How Face Masks Work to Prevent Transmission
Face masks primarily serve as a physical barrier that helps block respiratory droplets, which are a common mode of transmission for viruses and bacteria. When an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, they release droplets containing pathogens into the air. Wearing a face mask can significantly reduce the distance these droplets travel, thereby lowering the risk of exposure for those nearby.
Types of Face Masks
There are various types of face masks, each with different effectiveness levels. The most common types include:
| Type of Mask | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Cloth Masks | Homemade or commercially made masks from fabric | Moderate; filters large droplets but less effective against smaller aerosols |
| Surgical Masks | Loose-fitting disposable masks used primarily in healthcare settings | High; designed to block large droplets and some smaller particles |
| N95 Respirators | Tight-fitting masks that filter out at least 95% of airborne particles | Very High; provides a higher level of filtration and fit |
The Role of Face Masks in Community Health
Widespread use of face masks can lead to a significant decrease in disease transmission within communities. When a large percentage of the population wears masks, it creates a form of herd immunity, where even those who are not wearing masks are indirectly protected due to the reduced viral load in the environment.
Additionally, face masks can serve as a visual reminder of the ongoing health crisis, encouraging individuals to adopt other preventive measures such as social distancing and hand hygiene. This collective behavior reinforces community responsibility and awareness, which are crucial for controlling outbreaks.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Mask Use
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of face masks in reducing the spread of respiratory viruses. For instance, a meta-analysis found that the consistent use of face masks can lead to a 79% reduction in the transmission of COVID-19. Furthermore, countries that mandated mask-wearing saw a significant decline in infection rates compared to those that did not.
The following chart illustrates the correlation between mask usage and COVID-19 case rates in various countries:
| Country | Mask Mandate | COVID-19 Case Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|---|
| Country A | Mandatory | 50 |
| Country B | Voluntary | 150 |
| Country C | None | 300 |
Best Practices for Mask Usage
To maximize the effectiveness of face masks in controlling disease spread, it is essential to follow best practices:
- Choose the Right Mask: Opt for masks with higher filtration capabilities, such as N95 respirators when available, especially in high-risk settings.
- Ensure Proper Fit: Masks should cover both the nose and mouth snugly without gaps. A secure fit enhances their effectiveness.
- Practice Consistent Usage: Wear your mask consistently, particularly in crowded or enclosed spaces where physical distancing is challenging.
- Maintain Hygiene: Wash cloth masks regularly and dispose of surgical masks appropriately after use to prevent contamination.
Conclusion
Face masks are a critical component in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, especially respiratory viruses. By understanding their mechanisms of action, types, and best practices, individuals can play a significant role in protecting themselves and their communities. As we continue to navigate public health challenges, adopting face masks as part of our daily routine is a simple yet effective way to contribute to overall community health and safety.