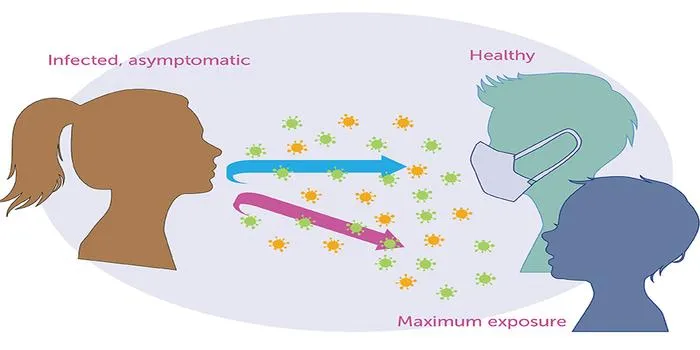
How Do Face Masks Control the Spread of Disease?
Face masks play a vital role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases, especially those transmitted through respiratory droplets. When worn correctly, face masks can significantly reduce the transmission of airborne pathogens, including viruses and bacteria. By acting as a physical barrier, masks help to block respiratory droplets that are expelled when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, thereby minimizing the risk of disease transmission to others.
What’s the Difference Between Sugar in Fruit and Sugar in Sweets and Candy?
When it comes to sugar, not all types are created equal. The sugar found in fruit and the sugar in sweets and candy differ significantly in terms of their nutritional impact and health effects. The primary distinction lies in their source and the way they are processed by the body.
A Model of the Cosmos
A Model of the Cosmos explores the philosophical and scientific theories that have shaped humanity's understanding of the universe. It delves into ancient cosmological views, the shift brought by the Copernican Revolution, and the impact of modern physics, like relativity and quantum mechanics. The work examines how these models influence our perception of reality and our place within the cosmos. It emphasizes the interplay between observation, theory, and cultural context in shaping our cosmic understanding.
What Causes Lunar and Solar Eclipses?
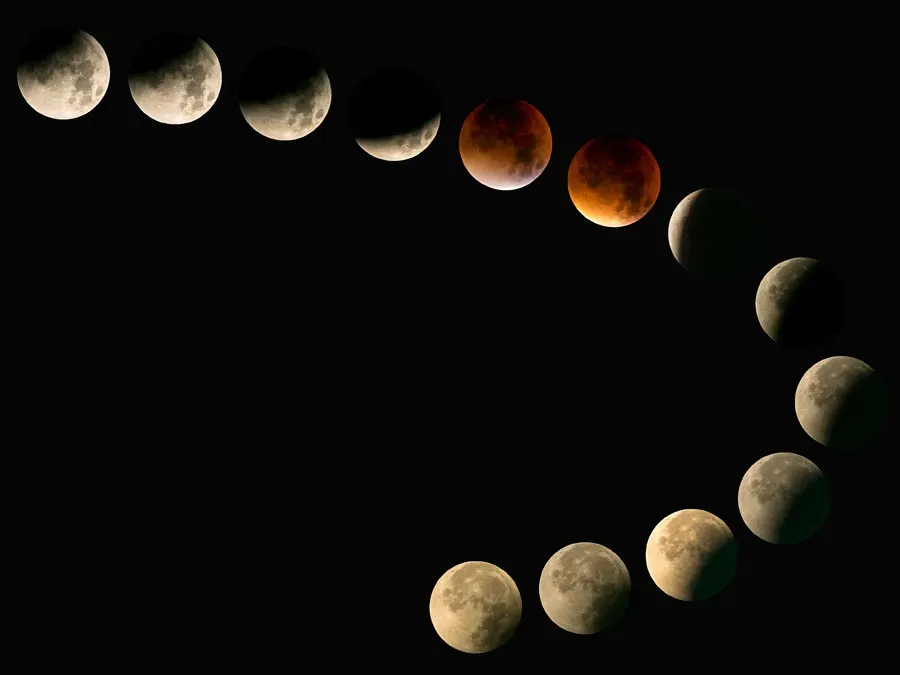
Lunar and solar eclipses occur due to the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth is directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is positioned between the Earth and the Sun, blocking sunlight and casting a shadow on the Earth. These celestial events depend on the precise orbits and alignments within the Earth-Moon-Sun system.
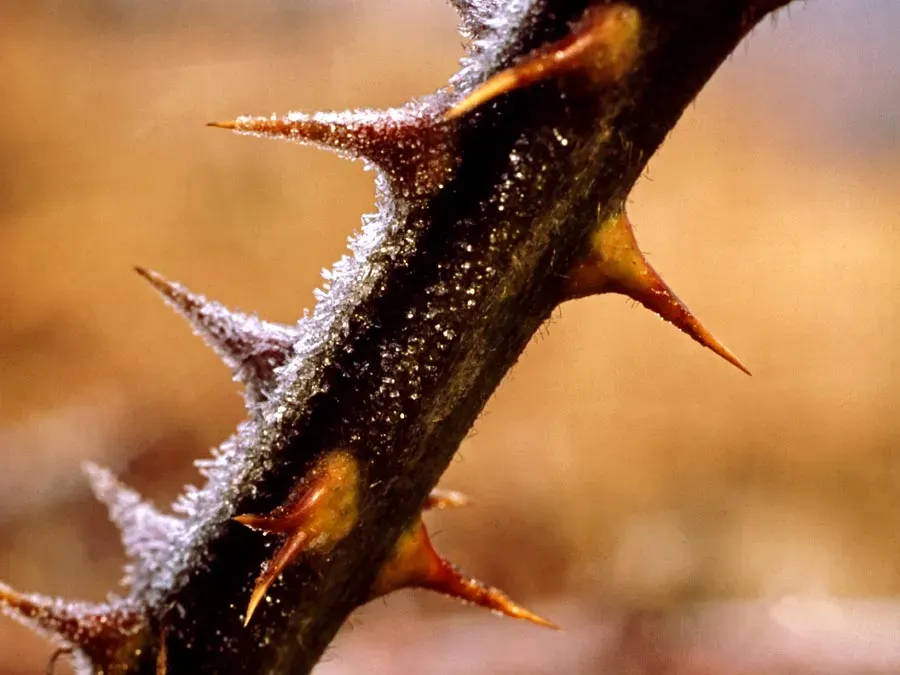
Botanical Barbarity: 9 Plant Defense Mechanisms
In "Botanical Barbarity: 9 Plant Defense Mechanisms," the article delves into the fascinating and often overlooked world of plant defenses. It explores how plants have evolved complex strategies to protect themselves from herbivores and environmental threats. These mechanisms range from producing toxic chemicals and thorns to emitting volatile organic compounds that attract predators of their attackers. Additionally, some plants employ mimicry and camouflage to avoid detection. This exploration reveals the intricate and dynamic relationships between plants and their ecosystems.
9 Ghostly Planets
Nine ghostly planets are mysterious celestial bodies that challenge our understanding of the universe. These enigmatic planets reside in distant solar systems, often shrouded in darkness and difficult to detect with conventional methods. Their eerie nature stems from their elusive orbits and faint visibility, which result in minimal interaction with their host stars. Despite their ghostly presence, they offer tantalizing insights into planetary formation and the diverse architectures of solar systems, expanding our knowledge of the cosmos.
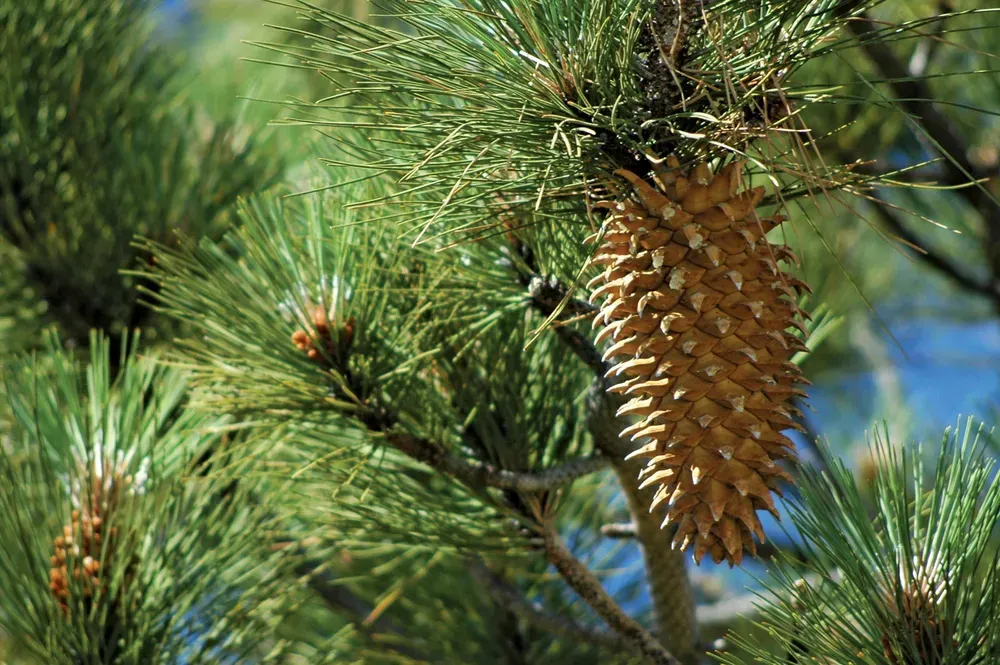
The 7 Best Pinecones (Really!)
Explore the fascinating world of pinecones with this engaging guide to the seven best varieties, highlighting their unique characteristics and beauty. Discover the majestic sugar pine, known for its impressive size, and the elegant Coulter pine, appreciated for its intricate design. Learn about the versatile lodgepole pine, often used in crafts, and the iconic Eastern white pine, celebrated for its classic appearance. This collection showcases the diversity of pinecones, offering insights into their ecological importance and aesthetic appeal.
Beyond Pi: 7 Underrated Single-Letter Variables and Constants
This article explores seven overlooked single-letter variables and constants that play crucial roles in mathematics and science beyond the famed pi. It delves into the significance of Euler's number in exponential growth and decay, the golden ratio's aesthetic appeal in art and nature, and the importance of Planck's constant in quantum mechanics. Other notable mentions include Avogadro's number in chemistry, the fine-structure constant in physics, the imaginary unit in complex numbers, and Boltzmann's constant in statistical mechanics.
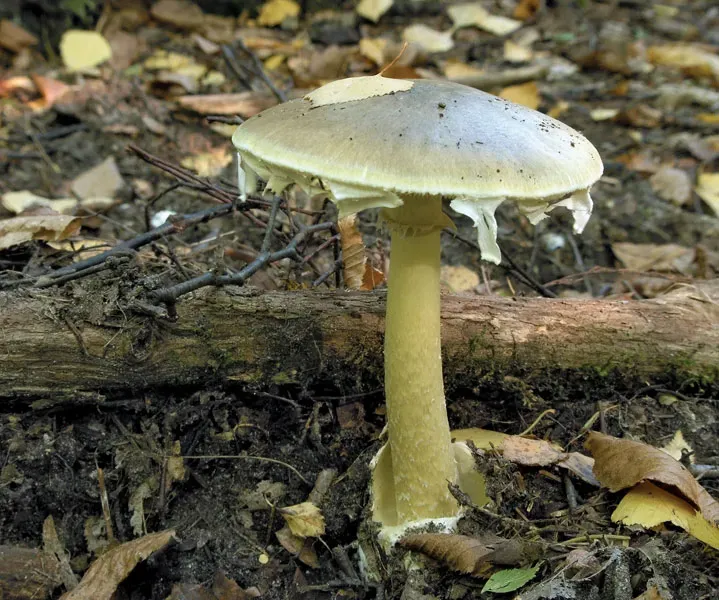
7 of the World’s Most Poisonous Mushrooms
Throughout the world, various mushrooms pose significant danger due to their toxic properties. The Death Cap is notorious for causing the majority of mushroom poisoning fatalities. The Destroying Angel is equally lethal, often mistaken for edible varieties. Autumn Skullcap contains deadly toxins that can lead to organ failure. The Deadly Dapperling is deceptively charming but highly poisonous. Fool’s Conecap can cause severe gastrointestinal distress. The Panther Cap has hallucinogenic properties alongside its toxicity. Lastly, the Jeweled Death Cap is both aesthetically appealing and perilous.
The 1916 Shark Attacks That Gave Sharks a Bad Rap
In the summer of 1916, a series of shark attacks along the New Jersey shore captured national attention and fueled widespread fear of sharks. Over twelve days, five individuals were attacked, with four fatalities, leading to a media frenzy that painted sharks as ruthless killers. The events significantly influenced public perception, embedding a deep-seated fear of sharks in popular culture. This period marked a turning point in the relationship between humans and sharks, contributing to their enduring reputation as menacing predators.
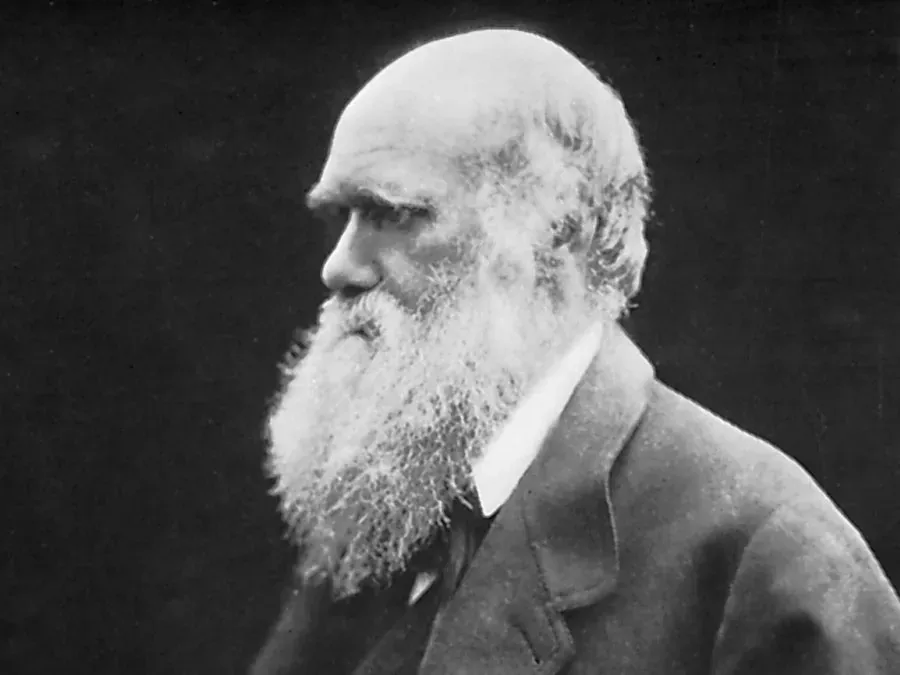
What Darwin Got Right (and Wrong) About Evolution
Charles Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection revolutionized our understanding of biology, providing insights into the diversity of life and the process of adaptation. He accurately identified the significance of variation and competition among species. However, Darwin lacked knowledge of genetic inheritance and the mechanisms of mutation, which are crucial for understanding evolution's intricacies. Modern science has expanded on Darwin's ideas, integrating genetics and molecular biology to offer a more comprehensive view of evolutionary processes.
7 of the World’s Deadliest Plants
Several plants are renowned for their deadly properties. The castor oil plant produces seeds containing ricin, a potent toxin. Oleander is highly toxic, with all parts capable of causing severe illness or death. Hemlock, used historically for executions, is extremely poisonous. Deadly nightshade contains atropine, leading to fatal outcomes. The rosary pea has seeds with abrin, a lethal substance. Water hemlock is one of North America's most toxic plants. The angel's trumpet contains scopolamine, known for its hallucinogenic and toxic effects.
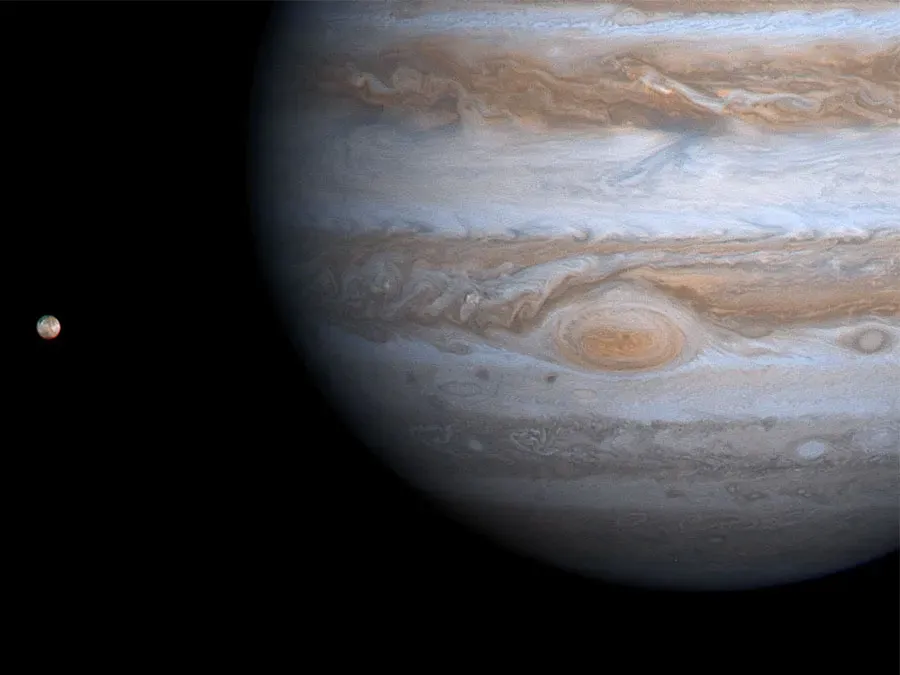
7 Important Dates in Jupiter History
Throughout history, key dates have marked significant milestones in our understanding of Jupiter. These include Galileo's discovery of its moons in 1610, which challenged geocentric views, and the 1973 flyby of Pioneer 10, the first spacecraft to reach Jupiter. The Voyager missions in 1979 provided detailed images and data, while the Galileo orbiter in 1995 explored its atmosphere and moons. The Juno mission, launched in 2011, continues to reveal unprecedented insights into Jupiter’s composition and magnetic field.
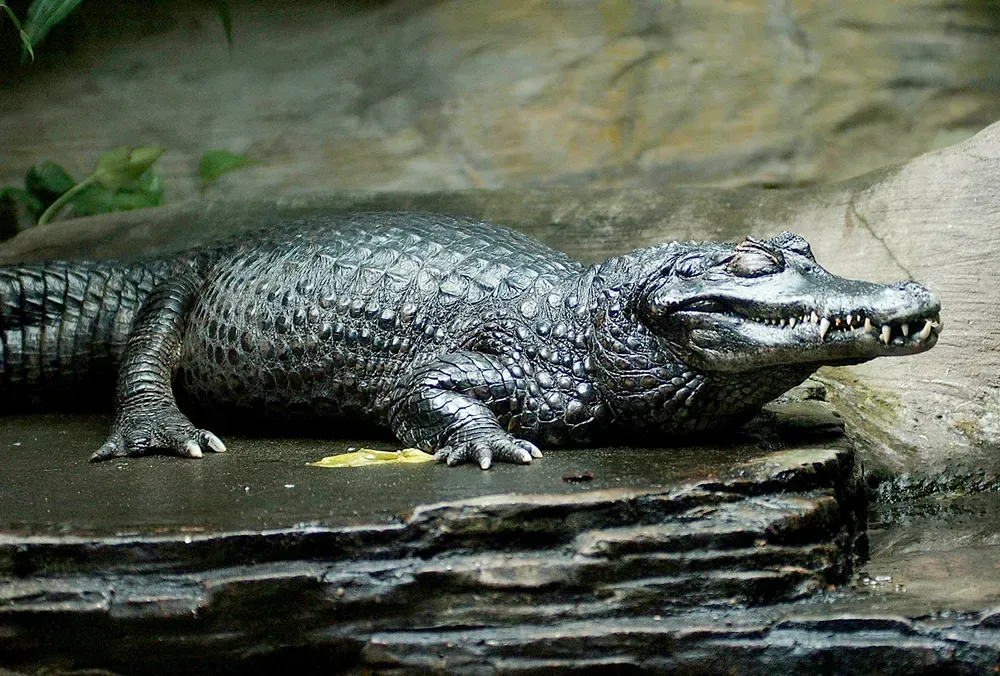
7 Crocodilian Species That Are Dangerous to Humans
Crocodilian species pose various threats to humans due to their size, strength, and territorial nature. The Nile crocodile, notorious for numerous attacks, is found across Africa's freshwater habitats. Saltwater crocodiles, the largest of their kind, inhabit Southeast Asia and Australia and are known for their aggressive behavior. American crocodiles, residing in the Americas, can be dangerous if provoked. The mugger crocodile, native to the Indian subcontinent, and the black caiman of the Amazon are also significant threats. Additionally, the Cuban crocodile and the Orinoco crocodile, though less widespread, are known for their potential danger to humans.
A Journey Through Time Since the Precambrian
A Journey Through Time Since the Precambrian explores the vast history of Earth, beginning with the ancient Precambrian era. It delves into the development of life from simple microorganisms to complex organisms, highlighting major evolutionary milestones and geological transformations. The narrative covers significant events such as the Cambrian Explosion, the rise and fall of dinosaurs, and the emergence of mammals and humans. This fascinating journey underscores the dynamic changes our planet has undergone over billions of years.
9 Celestial Omens
"9 Celestial Omens" explores a series of prophetic phenomena believed to influence human destiny and natural events. These omens, rooted in various ancient cultures, often involve astronomical occurrences such as eclipses, comets, and planetary alignments. Each omen is interpreted as a message or warning from the cosmos, foretelling significant changes or events in the world. This concept highlights humanity's enduring fascination with the heavens and the belief that celestial movements can impact earthly life in profound ways.
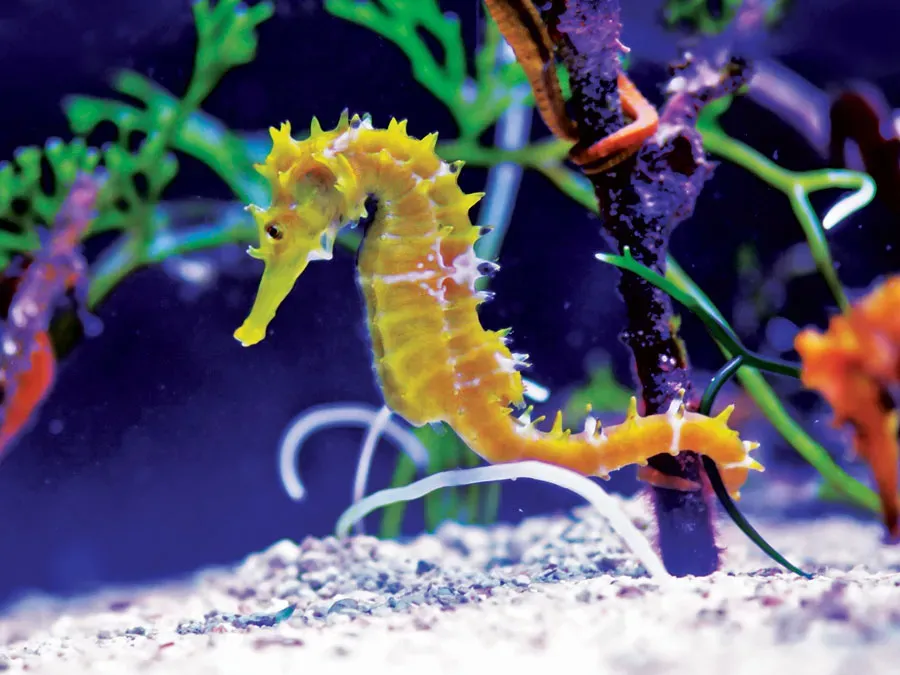
9 Fish Named After Other Animals
In the fascinating world of aquatic life, certain fish species are intriguingly named after other animals due to their physical resemblances or unique behaviors. The lionfish, with its striking mane-like fins, is a notable example. The parrotfish, known for its beak-like mouth, resembles a parrot. The catfish, with whisker-like barbels, mimics a cat. The elephantfish, recognized for its trunk-like snout, and the seahorse, with its equine shape, continue this trend, highlighting nature's creativity in naming.
10 Places to Visit in the Solar System
Explore the wonders of our solar system with a journey through ten fascinating destinations. Marvel at the towering peaks of Olympus Mons on Mars and the swirling clouds of Jupiter's Great Red Spot. Dive into the icy oceans of Europa and bask in the sulfuric beauty of Io. Experience the enigmatic hexagon storm on Saturn and the dazzling rings of Uranus. Witness the blue hues of Neptune and the mysterious Kuiper Belt. Each location offers a unique glimpse into the universe's natural marvels.
Exploring 7 of Earth’s Great Mountain Ranges
Embark on a journey through seven of Earth's most majestic mountain ranges, each offering unique landscapes and ecosystems. The Himalayas, home to Mount Everest, tower with awe-inspiring peaks. The Andes stretch along South America, rich in cultural history. North America's Rockies boast vast wilderness and diverse wildlife. Europe's Alps blend breathtaking scenery with vibrant traditions. The African Atlas Mountains offer rugged beauty. The Great Dividing Range in Australia showcases varied terrains, while Antarctica's Transantarctic Mountains present icy grandeur.
How Do Monkeys and Apes Trim Their Fingernails?
Monkeys and apes typically maintain their fingernails through natural wear and grooming behaviors. They often use their teeth to bite off excess nail growth, which helps keep their nails at a manageable length. Additionally, their active lifestyle, including climbing, foraging, and interacting with their environment, naturally abrades and trims their nails. Grooming, both self-performed and social, plays a critical role in nail maintenance, as these primates meticulously clean and manage each other's nails during social interactions.