- Home >
- Science
- > Technology
How Do Monkeys and Apes Trim Their Fingernails?
Monkeys and apes typically maintain their fingernails through natural wear and grooming behaviors. They often use their teeth to bite off excess nail growth, which helps keep their nails at a manageable length. Additionally, their active lifestyle, including climbing, foraging, and interacting with their environment, naturally abrades and trims their nails. Grooming, both self-performed and social, plays a critical role in nail maintenance, as these primates meticulously clean and manage each other's nails during social interactions.
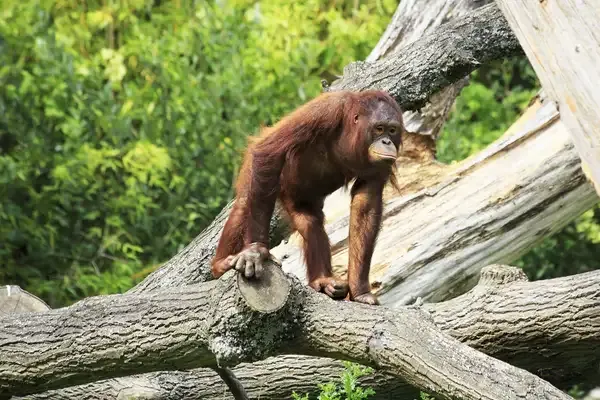

Monkeys and apes, as fascinating primates, have developed unique behaviors and techniques for grooming themselves, including the trimming of their fingernails. While they don’t have manicure tools like humans, these animals use their natural instincts and social behaviors to maintain their claws. Understanding how these creatures manage their fingernail care can provide insight into their grooming habits and social interactions.
The Importance of Nail Care in Primates
Nail care is crucial for the overall health and well-being of monkeys and apes. Long or jagged nails can lead to injuries, hinder movement, and affect their ability to climb or forage for food. Grooming serves multiple purposes:
- Hygiene: Regular grooming helps remove dirt, parasites, and dead skin cells.
- Social Bonding: Grooming is a social activity that strengthens relationships among group members.
- Physical Maintenance: Keeping nails in check promotes better mobility and agility.
Methods of Nail Trimming in Monkeys and Apes
Monkeys and apes utilize several methods for trimming their fingernails. Here are some of the most common practices.
| Method | Description | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Grooming | Primates use their teeth to bite and wear down their nails. | Common among many species |
| Social Grooming | Group members groom each other, which can include trimming nails. | Found in chimpanzees and macaques |
| Natural Wear | Activity such as climbing and foraging naturally wears down nails. | Observed in many arboreal species |
Self-Grooming: The Individual Approach
Self-grooming is a common behavior where monkeys and apes use their teeth to manage their fingernails. This method allows them to bite off any excess nail length or to smooth out rough edges. This behavior is often observed in species that may not have consistent social interactions, allowing them to maintain their nails independently. Self-grooming is not just limited to fingernails; it also includes cleaning fur and skin, showcasing the multifaceted nature of their grooming habits.
Social Grooming: A Community Effort
Social grooming, also known as allogrooming, is another vital method through which primates care for their nails. In this practice, one individual grooms another, which can involve trimming nails as well. This behavior is particularly prevalent among species like chimpanzees and macaques, where social bonds are essential for group cohesion. Grooming sessions can last for hours and often include a variety of grooming tasks, promoting both hygiene and social bonding.
Natural Wear: A Practical Solution
Interestingly, many monkeys and apes benefit from natural wear as a way to keep their nails trimmed. Activities such as climbing trees, foraging for food, and moving through their environment help to naturally file down their nails. This method is especially effective for species that spend a significant portion of their time in arboreal habitats, where constant movement can wear down sharp nails over time.
Health Considerations and Nail Care
Maintaining proper nail length is crucial for the health of monkeys and apes. Long nails can cause injuries, impede movement, and lead to complications such as infection. In captivity, where natural wear may be limited, caretakers often take special measures to ensure that these animals do not suffer from overgrown nails. This can include providing surfaces that encourage natural wear or, in some cases, veterinary interventions when necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the methods by which monkeys and apes trim their fingernails are integral to their grooming routines and overall health. Whether through self-grooming, social interactions, or natural wear, these primates exhibit a range of behaviors that help them maintain their nails. Understanding these practices not only sheds light on their daily lives but also emphasizes the importance of proper care in both wild and captive environments.
For those interested in the fascinating world of primates, observing their grooming habits can provide a deeper appreciation for their intelligence and social structures. As we continue to study these remarkable creatures, we gain valuable insights into their lives and the evolutionary significance of their grooming behaviors.