- Home >
- Science
- > Technology
What Darwin Got Right (and Wrong) About Evolution
Charles Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection revolutionized our understanding of biology, providing insights into the diversity of life and the process of adaptation. He accurately identified the significance of variation and competition among species. However, Darwin lacked knowledge of genetic inheritance and the mechanisms of mutation, which are crucial for understanding evolution's intricacies. Modern science has expanded on Darwin's ideas, integrating genetics and molecular biology to offer a more comprehensive view of evolutionary processes.
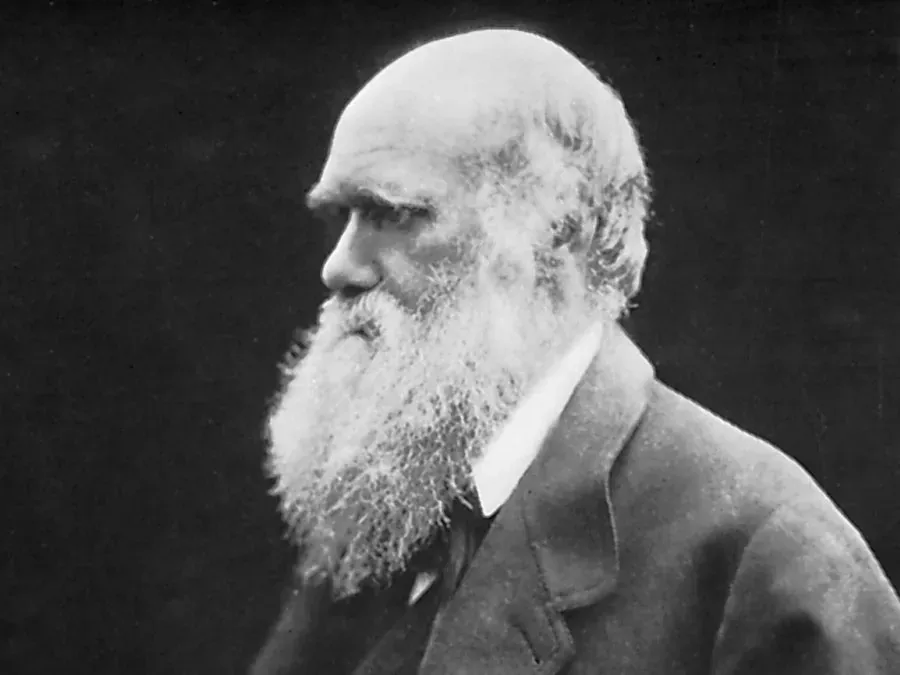

The theory of evolution, first articulated by Charles Darwin in the 19th century, has undergone considerable scrutiny and development since its inception. While Darwin laid the groundwork for our understanding of biological change over time, modern science has both validated and refined many of his ideas. This article will explore what Darwin got right and wrong about evolution, providing a balanced view of his contributions to the field of biology.
What Darwin Got Right
Darwin's most significant contribution to science was the concept of ''natural selection''. This mechanism explains how species adapt to their environments over generations. Here are some key points that illustrate what Darwin got right:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Natural Selection | Darwin proposed that individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing these traits to the next generation. |
| Descent with Modification | This idea suggests that all species share a common ancestor and that species evolve over time through gradual changes. |
| Variation in Populations | Darwin emphasized the importance of variation within species, which is crucial for natural selection to occur. |
| Adaptation | He correctly identified that adaptations occur over time, enabling species to thrive in specific environments. |
These foundational concepts remain central to the field of ''evolutionary biology''. Modern research continues to support the idea of ''natural selection'', demonstrating that it plays a crucial role in shaping the diversity of life on Earth.
What Darwin Got Wrong
Despite his groundbreaking insights, Darwin's theories were not without flaws. Some of the key areas where he fell short include:
| Concept | Misconception |
|---|---|
| Inheritance of Traits | Darwin lacked a clear understanding of ''genetics''. He believed in blending inheritance, where offspring were a mix of their parents' traits, rather than the discrete inheritance patterns later identified by Gregor Mendel. |
| Speed of Evolution | Darwin underestimated the speed at which evolution could occur. Modern findings suggest that evolution can happen rapidly in response to environmental changes, a concept known as ''punctuated equilibrium''. |
| Role of Chance | Darwin did not fully appreciate the role of ''genetic drift'' and other stochastic processes that can influence evolution, particularly in small populations. |
These misconceptions highlight the limitations of Darwin's understanding of the underlying mechanisms of evolution, which have been clarified through advancements in ''molecular biology'' and ''genetics''.
Modern Perspectives on Evolution
Since Darwin's time, our understanding of evolution has expanded significantly. The following concepts have emerged, refining and enhancing the foundational ideas laid out by Darwin:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Modern Synthesis | This framework integrates Darwin's theory of natural selection with Mendelian genetics, providing a more comprehensive view of how evolution operates. |
| Genomic Studies | Advancements in DNA sequencing have allowed scientists to trace evolutionary relationships at the molecular level, confirming and refining Darwin's ideas. |
| Epigenetics | This field explores how environmental factors can influence gene expression, introducing an additional layer of complexity to our understanding of evolution. |
These modern developments show that while Darwin was correct in many aspects of his theory, scientific progress has revealed a more intricate picture of evolution than he could have imagined. The integration of ''genetics'', ''epigenetics'', and various evolutionary mechanisms has enriched our understanding of how life evolves on Earth.
Conclusion
In summary, Charles Darwin made monumental contributions to our understanding of evolution, particularly through his insights into natural selection and adaptation. However, some of his ideas have been revised or expanded upon as our scientific knowledge has advanced. While he laid the groundwork for evolutionary biology, contemporary research continues to refine and redefine our understanding of the mechanisms driving evolution. Recognizing both what Darwin got right and wrong allows us to appreciate the complexity of life and the ongoing quest for knowledge in the field of biology.