- Home >
- Science
- > Technology
How Does the Human Body Maintain Its Temperature?
The human body maintains its temperature through a process called thermoregulation. This involves the hypothalamus, which acts as a thermostat, detecting changes in body temperature and initiating responses. When the body is too hot, it triggers sweating and vasodilation to release heat. Conversely, if the body is too cold, it induces shivering and vasoconstriction to conserve heat. These mechanisms, along with behavioral responses like seeking shade or warmth, help keep the body's temperature stable.
Advertisement
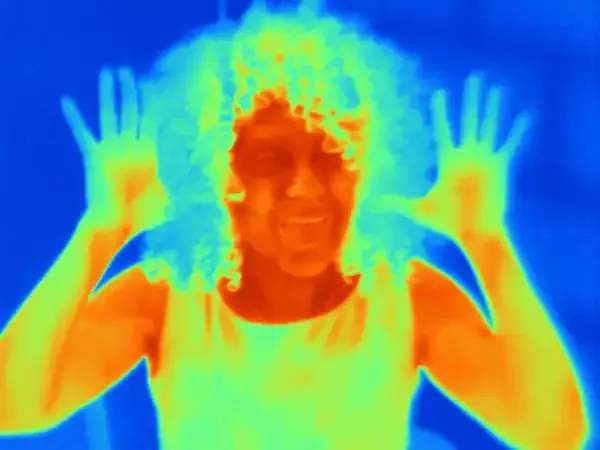

Understanding Thermoregulation: How the Human Body Maintains Its Temperature
The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, equipped with intricate systems that perform numerous functions to ensure survival. One of the most critical of these functions is thermoregulation, the process through which the body maintains its core temperature within a narrow, optimal range. This remarkable ability allows the body to adapt to various environmental conditions and maintain homeostasis, which is crucial for the proper functioning of enzymes and cellular processes. In this article, we will explore the mechanisms behind thermoregulation and the factors influencing it, offering insights into how the body preserves its temperature balance.
The Role of the Hypothalamus in Temperature Regulation
At the heart of the body's temperature control system is the hypothalamus, a small region located at the base of the brain. Often referred to as the body's thermostat, the hypothalamus detects changes in internal and external temperatures through signals from the skin and other sensory receptors. It processes this information and initiates responses to either dissipate excess heat or conserve heat as needed.
When the body is exposed to cold environments, the hypothalamus triggers mechanisms to generate and retain heat. For example, it can induce shivering, which involves rapid, involuntary muscle contractions that produce heat. Additionally, it can constrict blood vessels near the surface of the skin, a process known as vasoconstriction, which minimizes heat loss by reducing blood flow to the skin.
Conversely, when exposed to hot environments, the hypothalamus activates cooling mechanisms. Sweating is the primary method of cooling, where sweat glands produce moisture that evaporates from the skin, taking heat with it. Simultaneously, the body can increase blood flow to the skin through vasodilation, allowing more heat to escape into the environment.
Factors Affecting Thermoregulation
Several factors can influence the body's ability to regulate its temperature. Age is a significant factor; infants and the elderly often have less efficient thermoregulation due to undeveloped or diminished physiological responses. Physical fitness and body composition also play roles, as muscle mass generates heat during activity, while body fat can provide insulation.
Environmental factors, such as humidity and wind, can impact how effectively the body cools itself. High humidity levels can impede the evaporation of sweat, making it harder to dissipate heat, while wind can enhance heat loss by increasing evaporation and convection.
The Impact of Dehydration and Nutrition
Proper hydration is essential for efficient thermoregulation. Dehydration can impair the body's ability to sweat and cool down, leading to heat exhaustion or heat stroke in extreme conditions. Thus, maintaining adequate fluid intake is crucial, especially during hot weather or intense physical activity.
Nutrition also plays a role in thermoregulation. A balanced diet provides the energy needed for metabolic processes that generate heat, while certain nutrients, like electrolytes, help maintain fluid balance and support nerve function, which is vital for thermoregulatory responses.
Conclusion
The human body's ability to maintain its temperature is a testament to its complex and efficient design. Through the coordinated efforts of the hypothalamus, the cardiovascular system, and various physiological responses, the body can adapt to changing environments and maintain homeostasis. Understanding the mechanisms of thermoregulation and the factors that influence it can empower individuals to better manage their health and wellbeing, particularly in extreme temperatures. Whether it's staying hydrated, dressing appropriately for the weather, or maintaining physical fitness, supporting the body's natural temperature regulation is key to optimal health.