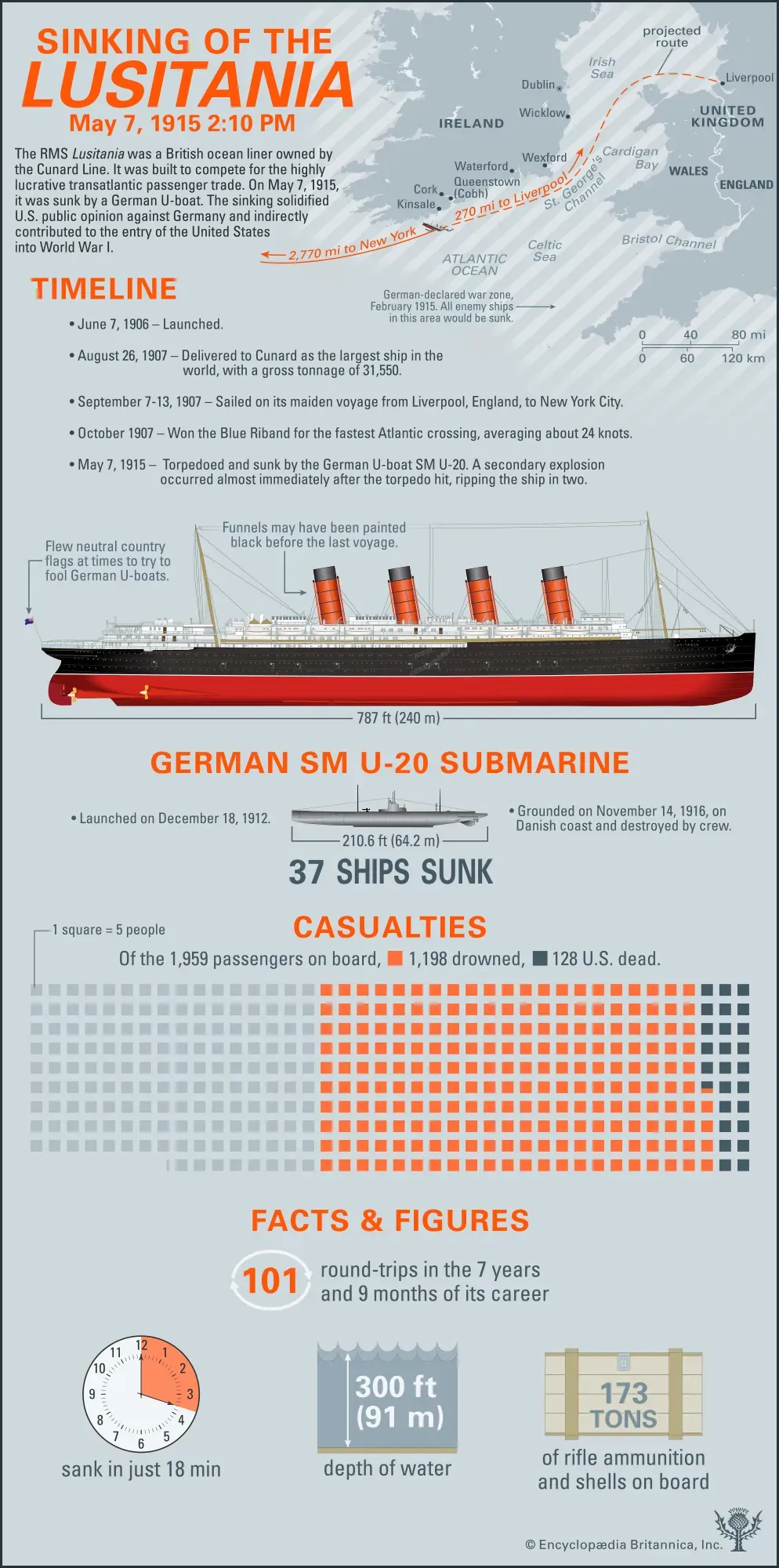
Why prescription drugs can work differently for different people
Prescription drugs can yield varying effects among individuals due to genetic differences, metabolism rates, and unique health conditions. Factors such as age, gender, and lifestyle choices also play a significant role in how medications interact with the body, leading to diverse outcomes in efficacy and side effects. Similarly, the origins of city nicknames often reflect historical, cultural, or geographical influences. For instance, "The Big Apple" signifies New York's prominence in the jazz scene, while other cities boast nicknames rooted in local lore or characteristics.
Advertisement
Prescription drugs can have varying effects on different people due to a multitude of factors that influence how a medication interacts with an individual's body. Understanding these differences is crucial for personalized medicine and optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
Factors Influencing Drug Efficacy and Response
One of the primary reasons prescription drugs can work differently is due to genetic variations among individuals. Genetic differences can affect how a person metabolizes a drug, which in turn influences the drug's effectiveness and the likelihood of side effects. For instance, certain genetic markers can make individuals metabolize drugs faster or slower than average, impacting the drug's concentration in the bloodstream.
Another important factor is an individual's age and sex. These can affect drug metabolism and distribution. For example, older adults may experience slower drug clearance, potentially increasing the risk of adverse effects. Similarly, hormonal differences between sexes can influence drug action and efficacy.
Body weight and composition also play significant roles in drug response. Drugs are often dosed based on weight and body mass, affecting how they are distributed in the body. Individuals with higher body fat percentages may store certain drugs longer, altering how the drug works and its potential side effects.
Lifestyle choices, such as diet, alcohol consumption, and smoking, can interact with medications, either enhancing or reducing their effectiveness. For example, a diet rich in certain foods might accelerate the metabolism of a drug, reducing its efficacy.
Moreover, existing health conditions can significantly impact how a drug works. Conditions like liver or kidney disease can impair the body's ability to process drugs, necessitating dosage adjustments. Additionally, drug interactions can occur when a person is taking multiple medications, leading to altered drug effectiveness or increased side effects.
Lastly, psychological factors such as stress and mental health conditions can influence drug response. Stress can affect drug metabolism and the body's overall physiological state, potentially altering drug effects.
In conclusion, the variability in drug response is a complex interplay of genetic, physiological, lifestyle, and psychological factors. Understanding these can help healthcare providers tailor treatments to individual needs, improving outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.