US-backed vaccine patent waiver: pros and cons explained
The US-backed vaccine patent waiver seeks to enhance global access to vaccines by temporarily suspending intellectual property protections, which could significantly boost vaccination rates in developing countries. However, critics argue it may undermine innovation and investment in pharmaceutical research. Meanwhile, the exploration of how cities like New York and others acquired their nicknames reveals fascinating historical and cultural narratives. Each nickname often reflects unique characteristics, events, or local legends that contribute to the city's identity and charm.
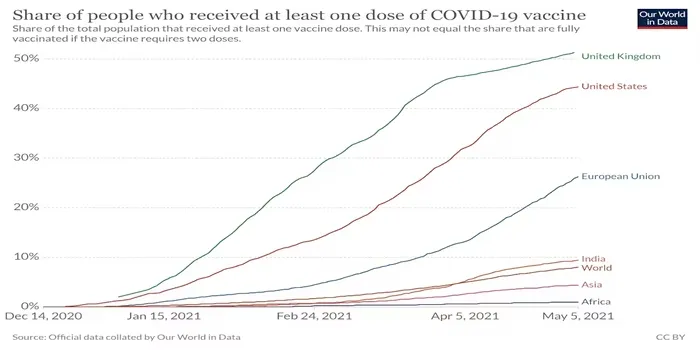
Understanding the US-backed Vaccine Patent Waiver
The global pandemic has highlighted the necessity for equitable access to vaccines. In response, the US has backed a proposal for a vaccine patent waiver aimed at increasing vaccine production in developing countries. This article explores the pros and cons of the US-backed vaccine patent waiver, shedding light on its potential impacts on global health and the pharmaceutical industry.
Pros of the Vaccine Patent Waiver
There are several significant advantages associated with the US-backed vaccine patent waiver, which could lead to an increase in vaccine accessibility worldwide.
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Vaccine Production | The waiver could allow more manufacturers in developing countries to produce vaccines, potentially increasing supply to meet global demand. |
| Equitable Access | By removing patent protections, vaccines can be made available to low-income countries, reducing health disparities. |
| Stimulating Local Economies | Local production of vaccines could create jobs and stimulate economic growth in regions that are currently dependent on donations or imports. |
| Encouraging Innovation | By fostering a competitive environment, the waiver could encourage innovation in vaccine development and production processes. |
Cons of the Vaccine Patent Waiver
While there are clear benefits to the waiver, it also comes with certain drawbacks that must be considered.
| Disadvantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Impact on Pharmaceutical Innovation | Critics argue that waiving patents could deter pharmaceutical companies from investing in research and development, ultimately slowing down innovation in vaccine technology. |
| Quality Control Concerns | With increased production, there may be concerns regarding the quality and safety of vaccines produced by manufacturers without established reputations. |
| Legal and Regulatory Challenges | Implementing a waiver could lead to complex legal and regulatory challenges, including disputes between countries and pharmaceutical companies. |
| Short-term vs Long-term Solutions | The waiver may provide a temporary solution to vaccine shortages but does not address the underlying issues related to global health infrastructure and preparedness. |
The Economic Implications
One of the most significant factors in the vaccine patent waiver debate is its economic implications. The pharmaceutical industry is a major contributor to global economies, and changes in patent laws could have ripple effects.
Proponents of the waiver argue that it could lead to lower vaccine prices, making them affordable for lower-income populations. However, opponents contend that the potential decrease in profits for pharmaceutical companies might result in reduced funding for future healthcare innovations.
Global Health Perspectives
From a global health perspective, the US-backed vaccine patent waiver could be a game-changer. With millions still unvaccinated against COVID-19 and other diseases, increasing production in developing countries could save countless lives.
However, achieving a balance between ensuring affordable access and maintaining a robust pharmaceutical industry remains a critical challenge. Policymakers must carefully consider how to implement the waiver to maximize benefits while minimizing potential downsides.
Conclusion
The US-backed vaccine patent waiver presents both opportunities and challenges in the quest for global vaccine equity. While the potential to increase vaccine production and accessibility is significant, it is essential to address the concerns surrounding pharmaceutical innovation, quality control, and legal implications.
As the world continues to navigate the complexities of the pandemic, finding a path that considers both public health needs and the sustainability of the pharmaceutical industry will be crucial. Ultimately, the success of the vaccine patent waiver will depend on collaborative efforts among governments, health organizations, and the private sector to ensure that vaccines are not only available but also safe and effective for all.