- Home >
- Science
- > Innovation
Why Does the United States Have More Tornadoes than Any Other Country?
The United States experiences more tornadoes than any other country primarily due to its unique geographical features. The combination of the Rocky Mountains and the Gulf of Mexico creates ideal conditions for tornado formation. Warm, moist air from the Gulf collides with cold, dry air from Canada and the Rockies, generating severe thunderstorms. The flat terrain of the Great Plains, often referred to as "Tornado Alley," allows these storms to intensify and spawn tornadoes more frequently.
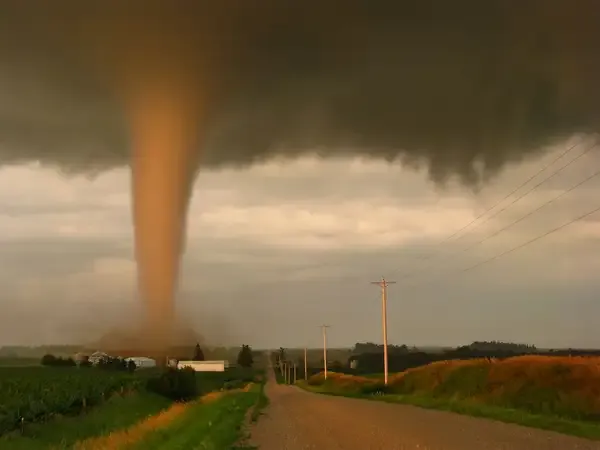

The United States is renowned for its dramatic weather phenomena, and one of the most striking is the tornado. Each year, the U.S. experiences more tornadoes than any other country, making it a focal point for meteorologists and weather enthusiasts alike. Understanding why the United States has such a high frequency of tornadoes involves examining geographical, climatic, and atmospheric factors that create the perfect conditions for these violent storms.
Geographical Factors Contributing to Tornado Formation
The geographical landscape of the United States is one of the primary reasons for the high incidence of tornadoes. The country features a vast expanse of flat plains, particularly in the central region known as "Tornado Alley." This area stretches from Texas through Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, and into parts of South Dakota. The flat terrain allows for the unrestricted movement of air masses, which is crucial for tornado development.
Additionally, the U.S. is bordered by two major bodies of water: the Atlantic Ocean to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. These oceans contribute to the varying weather patterns that can lead to tornado formation. Warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico frequently collides with cooler, dry air from Canada, creating ideal conditions for severe thunderstorms, which can spawn tornadoes.
Climatic Conditions Favoring Tornadoes
The climate in the United States varies significantly from region to region, but some areas experience conditions that are particularly conducive to tornado development. The ''Great Plains'', for example, have a continental climate characterized by hot summers and cold winters. This temperature contrast between seasons creates instability in the atmosphere, which is a critical factor in tornado formation.
During the spring months, these temperature differences are most pronounced. Warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico begins to surge northward, while cooler air from the north remains in place. This clash of air masses can lead to the development of supercell thunderstorms, which are often responsible for producing the most violent tornadoes.
The Role of Atmospheric Conditions
In addition to geographical and climatic factors, specific atmospheric conditions play a crucial role in tornado formation. The presence of ''wind shear'' is particularly important. Wind shear refers to the change in wind speed and direction at different altitudes. When wind shear is strong, it can create a rotating effect in the atmosphere that can lead to the development of tornadoes.
Moreover, the ''jet stream'', a fast-flowing ribbon of air in the atmosphere, often contributes to severe weather patterns in the U.S. During the spring months, the jet stream tends to dip further south, enhancing the instability and creating the conditions necessary for severe thunderstorms and potential tornadoes.
Statistics and Tornado Frequency
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the United States averages around 1,000 tornadoes each year, significantly more than any other country. Here’s a simple table illustrating the average annual tornado occurrences in various countries:
| Country | Average Annual Tornadoes |
|---|---|
| United States | 1,000+ |
| Canada | 100 |
| United Kingdom | 30 |
| Australia | 10 |
This stark contrast in tornado frequency underscores the unique environmental conditions present in the U.S. that facilitate tornado formation. Other countries may experience tornadoes, but none match the sheer volume seen in the United States.
Impact of Tornadoes on Communities
With the high frequency of tornadoes in the U.S. comes significant implications for communities. Tornadoes can cause devastating damage to property and infrastructure, leading to loss of life and extensive economic costs. The ''National Weather Service (NWS)'' plays a critical role in monitoring and issuing warnings to help mitigate these impacts. Advances in technology and meteorological research have improved the accuracy of tornado forecasting, allowing communities to prepare and respond more effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, the combination of geographical features, climatic conditions, and atmospheric dynamics makes the United States uniquely susceptible to tornadoes. With more tornadoes occurring here than in any other country, the need for continued research and preparedness is paramount. Understanding these factors not only enhances our knowledge of tornadoes but also aids in the development of better safety measures for communities at risk.
As we continue to study these extraordinary weather phenomena, we can better appreciate the science behind tornadoes and work towards improving safety and response strategies for those in tornado-prone regions.