- Home >
- Pop
- > Fashion Trends
What’s the Difference Between Cane Sugar and Beet Sugar?
Cane sugar and beet sugar are both sucrose but differ in their sources and production processes. Cane sugar is derived from sugarcane, primarily grown in tropical climates, while beet sugar comes from sugar beets, which thrive in temperate regions. The refining processes also vary slightly, influencing taste and texture. In contrast, cities often acquire nicknames based on historical, cultural, or geographical attributes. For instance, New York City is known as "The Big Apple," reflecting its vibrant culture and significance in the music industry.
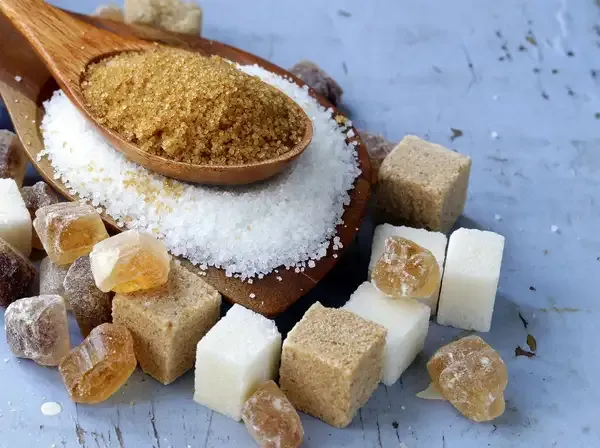

Cane sugar and beet sugar are two common types of sugars that are widely used in the food and beverage industry. While they serve similar purposes in cooking and baking, there are distinct differences between them. Understanding these differences can help consumers make informed choices about their sugar intake and the products they choose to purchase. This article will explore the key differences between cane sugar and beet sugar, including their sources, production processes, and nutritional profiles.
Source of Sugar
Cane sugar is derived from the sugarcane plant, which grows in tropical and subtropical climates. The sugarcane stalks are harvested, crushed, and processed to extract the juice, which is then refined into sugar. In contrast, beet sugar is extracted from sugar beets, which are root vegetables that thrive in temperate climates. The beets are harvested, sliced, and processed to extract the sugar, which is also refined into granulated sugar. Both types of sugar are primarily composed of sucrose, but their sources influence their taste and potential applications.
Production Process
The production processes for cane sugar and beet sugar differ significantly, impacting their final characteristics. Cane sugar production involves several steps:
- Harvesting: Mature sugarcane stalks are cut and collected.
- Crushing: The stalks are crushed to extract the juice.
- Clarification: The juice is heated and clarified to remove impurities.
- Evaporation: The juice is evaporated to concentrate the sugar content.
- Crystallization: The concentrated syrup is cooled to form sugar crystals.
- Refinement: The crystals are further refined to produce the final product.
Beet sugar production follows a similar process, but with some variations:
- Harvesting: Sugar beets are dug up from the ground.
- Slicing: The beets are sliced into thin strips to facilitate extraction.
- Extraction: Hot water is used to extract the sugar from the sliced beets.
- Purification: The extracted juice is purified and concentrated.
- Crystallization: Like cane sugar, the syrup is crystallized to form sugar.
- Refinement: The final product is refined to remove any remaining impurities.
Nutritional Profile
When it comes to nutrition, cane sugar and beet sugar are quite similar, as both are primarily composed of sucrose. However, some differences may exist in trace minerals and flavor profiles:
| Aspect | Cane Sugar | Beet Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Slightly more aromatic, with a subtle molasses flavor | Cleaner, more neutral taste |
| Minerals | May contain trace amounts of minerals like calcium and potassium | Typically lower in trace minerals |
| Color | Can vary from white to brown, depending on refining | Mostly white, with minimal color variations |
Environmental Impact
The cultivation of sugarcane and sugar beets also has environmental implications. Sugarcane is often grown in large monocultures, which can lead to soil degradation, water depletion, and the use of pesticides. In contrast, sugar beets are typically grown in temperate regions and may require less water than sugarcane. However, the use of fertilizers and pesticides in beet farming can also have negative environmental effects. Choosing organic or sustainably sourced sugar can help mitigate some of these concerns.
Uses and Applications
Both cane sugar and beet sugar are used in a variety of food products, including sweets, beverages, and baked goods. However, due to their subtle flavor differences, some chefs and bakers may prefer one over the other for specific applications. Cane sugar's slightly richer flavor can enhance certain desserts, while beet sugar's neutral taste may be favored in recipes where the sweetness needs to be prominent without additional flavors.
Cost and Availability
In terms of cost and availability, cane sugar is often more readily available in tropical regions, while beet sugar is more common in temperate regions. Prices can fluctuate based on agricultural yields, market demand, and production costs. Generally, both types of sugar are competitively priced, making them accessible to consumers worldwide.
Conclusion
In summary, while cane sugar and beet sugar share many similarities, they are distinct in terms of their sources, production methods, nutritional profiles, and environmental impacts. Understanding these differences can help consumers make informed choices about the types of sugar they use in their cooking and baking. Whether you prefer the aromatic flavor of cane sugar or the neutral taste of beet sugar, both options can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.