- Home >
- Pop
- > Fashion Trends
What’s the Difference Between Sweet Potatoes and Yams?
Sweet potatoes and yams, often confused, differ in origin and texture. Sweet potatoes are starchy tubers with smooth skin, while yams are starchy tubers with rough skin, primarily found in Africa and the Caribbean. Meanwhile, cities like New York, famously known as "The Big Apple," have intriguing stories behind their nicknames, reflecting cultural, historical, or geographical significance. Other notable cities also possess unique monikers, often revealing insights into their identity and the characteristics that set them apart.
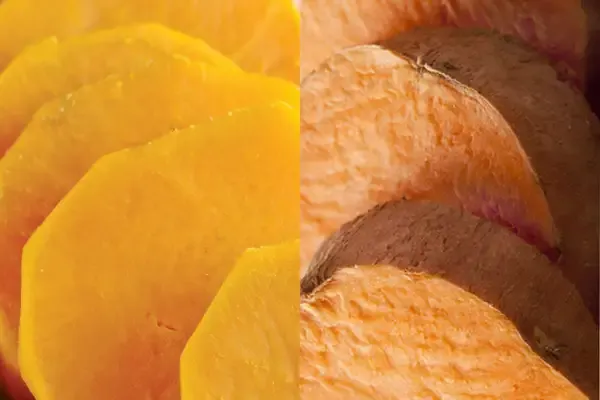

Understanding Sweet Potatoes and Yams
When it comes to root vegetables, ''sweet potatoes'' and ''yams'' are often confused due to their similar appearances and uses in cooking. However, they are distinct in terms of botanical classification, taste, texture, and nutritional value. Understanding these differences can enhance your culinary experiences and help you make informed dietary choices.
Botanical Classifications
The primary difference lies in their botanical classifications. ''Sweet potatoes'' belong to the Convolvulaceae family, while ''yams'' are part of the Dioscoreaceae family. In the United States, the term "yam" is commonly used to refer to orange-fleshed sweet potatoes, but true yams are native to Africa and Asia, and they have a different structure and flavor.
Physical Characteristics
Here’s a breakdown of their physical characteristics:
| Characteristic | Sweet Potatoes | Yams |
|---|---|---|
| Skin Color | Reddish-brown, yellow, or purple | Brown or dark, bark-like skin |
| Flesh Color | Orange, yellow, or purple | White, purple, or yellow |
| Texture | Soft and creamy when cooked | Starchy and dry |
Taste Profiles
The ''taste'' of sweet potatoes and yams differs significantly. Sweet potatoes are known for their ''sweetness'' and creaminess, making them ideal for both savory and sweet dishes. They can be roasted, mashed, or even used in desserts. On the other hand, yams have a more earthy and starchy flavor, often described as less sweet and more neutral. This allows them to pair well with savory dishes, but they are not commonly used in desserts.
Nutritional Value
When comparing the ''nutritional value'' of sweet potatoes and yams, both offer health benefits but differ in specific nutrients. Below is a simple comparison chart:
| Nutrient | Sweet Potatoes (1 medium) | Yams (1 medium) |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 112 | 157 |
| Carbohydrates | 26 g | 37 g |
| Fiber | 4 g | 6 g |
| Vitamin A | Sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene, providing 400% of the daily value. | Low in Vitamin A |
| Vitamin C | 30% of daily value | 28% of daily value |
As seen in the chart, ''sweet potatoes'' are particularly high in Vitamin A, which is essential for maintaining healthy vision and immune function. They also provide a good amount of fiber, which supports digestive health. Yams, while higher in calories and carbohydrates, offer their own set of nutrients that can be beneficial in a balanced diet.
Culinary Uses
Both sweet potatoes and yams can be used in a variety of culinary contexts, but their unique flavors and textures lend themselves to different dishes. Here are some popular uses for each:
- Sweet Potatoes: Used in casseroles, pies, fries, soups, and as a side dish. They are often mashed or baked and can even be added to smoothies for extra sweetness and nutrients.
- Yams: Commonly found in savory dishes, yams can be boiled, roasted, or used in stews. They are a staple in Caribbean and West African cuisines.
Conclusion
In summary, while ''sweet potatoes'' and ''yams'' may look similar, they are fundamentally different in terms of classification, taste, and nutrition. Sweet potatoes are sweeter and more versatile, while yams offer a starchy alternative for savory dishes. By knowing the differences, you can enhance your cooking and enjoy the unique flavors each vegetable offers.
So the next time you’re at the grocery store or planning a meal, remember the distinctions between sweet potatoes and yams to make the best choice for your culinary needs!