- Home >
- Science
- > Innovation
What’s the Difference Between a Grasshopper and a Cricket?
Grasshoppers and crickets both belong to the order Orthoptera, yet they differ in several ways. Grasshoppers tend to have shorter antennae, and they are primarily active during the day, whereas crickets have long antennae and are mostly nocturnal. Grasshoppers usually produce sound by rubbing their hind legs against their wings, while crickets create chirping sounds by rubbing their wings together. Additionally, grasshoppers are known for their powerful jumping abilities, while crickets are less adept jumpers.
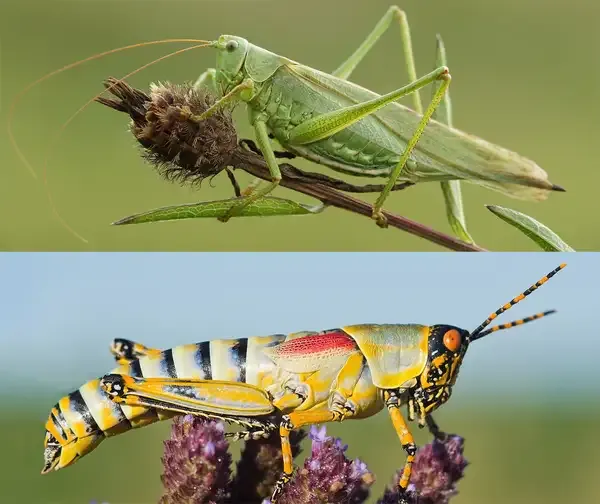

When it comes to the world of insects, grasshoppers and crickets are two of the most fascinating and often confused creatures. Both belong to the order Orthoptera, but they exhibit distinct differences that set them apart. Understanding these differences can enhance your knowledge of these remarkable insects. Below, we delve into the key characteristics that distinguish grasshoppers from crickets.
Physical Characteristics
One of the most apparent differences between grasshoppers and crickets is their physical appearance. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Grasshopper | Cricket |
|---|---|---|
| Body Shape | More elongated and slimmer | Stout and robust |
| Antennas | Shorter, often less than the body length | Longer, usually several times the body length |
| Wings | Some species have wings that are used for flying | Often have wings, but many species are flightless |
| Color | Often green or brown, blending in with vegetation | Usually darker, often brown or black |
Behavioral Differences
Grasshoppers and crickets also exhibit different behaviors that reflect their unique adaptations and lifestyles:
| Behavior | Grasshopper | Cricket |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding Habits | Herbivorous, primarily feeding on grass and leaves | Omnivorous, feeding on plant material, fungi, and other organic matter |
| Activity Time | Mostly diurnal (active during the day) | Nocturnal (active at night) |
| Mating Calls | Generally silent, rely on visual signals | Produce loud chirping sounds to attract mates |
| Jumping Ability | Powerful jumpers, can leap several times their body length | Less capable of jumping, prefer to walk or crawl |
Habitat Preferences
Another aspect where grasshoppers and crickets differ is their habitat preferences. Understanding where they thrive can provide insight into their ecological roles:
| Aspect | Grasshopper | Cricket |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred Environment | Open fields, meadows, and grasslands | Woodlands, underbrush, and damp areas |
| Temperature Tolerance | Prefer warmer climates | Can tolerate cooler temperatures |
Life Cycle
Both grasshoppers and crickets undergo similar life cycles, but there are noteworthy differences:
| Life Cycle Stage | Grasshopper | Cricket |
|---|---|---|
| Egg Stage | Eggs are laid in pods in the soil | Eggs are laid in moist soil or plant material |
| Nymph Stage | Hatchlings resemble miniature adults and undergo several molts | Nymphs also resemble adults, but may take longer to mature |
| Adult Stage | Reach adulthood in 4-6 weeks | May take several months to reach maturity |
Conclusion
In summary, while grasshoppers and crickets share a common lineage and some similarities, their differences in physical characteristics, behaviors, habitat preferences, and life cycles illustrate the diversity within the Orthoptera order. Recognizing these distinctions can enrich your understanding of these insects and their roles in the ecosystem.
Whether you are a budding entomologist or simply someone interested in nature, knowing the differences between grasshoppers and crickets can enhance your appreciation for these remarkable creatures. For more insights and information on various species and their habitats, be sure to explore further!