- Home >
- Health
- > Epidemiology
What Is a Superspreader Event?
A superspreader event refers to a situation where a single individual infects a disproportionately large number of people, often during gatherings or crowded environments, leading to rapid disease transmission. In "The Big Apple," the term highlights New York City's vibrant culture and significant influence. Similarly, other famous cities have unique nicknames that reflect their history, characteristics, and cultural essence, creating a rich tapestry of identity for each location, from the Windy City to the City of Lights.
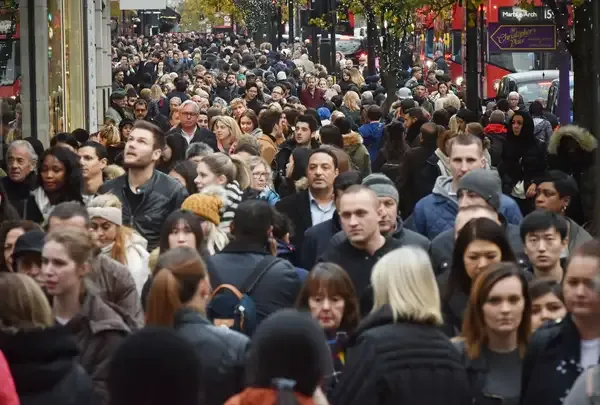

In the context of infectious diseases, a superspreader event refers to a gathering or situation where a single individual infects a disproportionately high number of other people. These events can lead to widespread transmission of a virus, making them a significant concern for public health officials. Understanding what constitutes a superspreader event is crucial for managing outbreaks effectively.
Characteristics of Superspreader Events
Several characteristics define a superspreader event:
- High Population Density: When many people gather in a confined space, the likelihood of transmission increases significantly.
- Duration of Contact: Longer interactions between individuals can facilitate the spread of pathogens.
- Environmental Factors: Certain environments, like poorly ventilated indoor settings, can enhance the risk of transmission.
- Infectiousness of the Individual: Some individuals may carry a higher viral load or exhibit more severe symptoms, making them more likely to spread infections.
Types of Superspreader Events
Superspreader events can take many forms. Below is a table showcasing different types of events that have been identified as superspreader scenarios:
| Event Type | Description | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Social Gatherings | Parties, weddings, and family gatherings where people come into close contact. | A wedding in Maine in August 2020 resulted in multiple COVID-19 cases. |
| Religious Services | Church services and other faith-based gatherings with large attendance. | A choir rehearsal in Washington state led to numerous infections. |
| Sporting Events | Games or events where fans gather in large numbers. | A football match in Italy was linked to a spike in cases. |
| Conventions and Conferences | Professional gatherings where attendees often travel from various locations. | A tech conference in California became a hotspot for COVID-19 transmission. |
Why Are Superspreader Events Important?
Understanding superspreader events is vital for several reasons:
- Public Health Response: Identifying potential superspreader events can help health authorities implement targeted interventions to prevent outbreaks.
- Resource Allocation: Knowing which events pose the greatest risk allows for efficient use of resources, such as testing and contact tracing.
- Community Awareness: Educating the public about the risks associated with certain gatherings can promote safer behaviors.
The Role of Technology in Managing Superspreader Events
Modern technology plays a significant role in managing and mitigating the impact of superspreader events. Applications and platforms that allow for contact tracing and symptom reporting can help identify potential outbreaks early on. For instance, the use of referrerAdCreative can aid in promoting public health messages effectively. By utilizing targeted advertisements, organizations can reach specific demographics to inform them about the dangers of superspreader events and how to avoid them.
Conclusion
Superspreader events are critical in the study of infectious diseases, particularly during outbreaks. By understanding the characteristics and implications of these events, public health officials can better formulate strategies to control the spread of infections. The importance of community vigilance, combined with technological advancements like referrerAdCreative, can significantly reduce the occurrence and impact of these events. Awareness and education are key to preventing superspreader events and protecting public health.