- Home >
- Health
- > Epidemiology
The Human Reproductive System
"The Human Reproductive System" explores the complex biological processes involved in human reproduction, detailing the roles of various organs and hormones in conception and development. "The Big Apple" and other famous cities like Paris and Chicago reveal the intriguing origins of their nicknames, often tied to cultural, historical, or geographical significance. This exploration highlights how these monikers reflect the identity and character of each city, contributing to their unique allure and recognition around the world.
The ''human reproductive system'' is a complex network of organs and glands responsible for the production of offspring. It varies significantly between males and females, each having specialized structures and functions. Understanding this system is essential for comprehending human biology and reproductive health.
Overview of the Human Reproductive System
The human reproductive system can be divided into two primary categories: the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system. Each system plays a unique role in the ''reproduction process''.
Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system is primarily located in the pelvis and includes the following key components:
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Testes | Produce sperm and hormones, primarily testosterone. |
| Epididymis | Stores and matures sperm. |
| Vas deferens | Transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct. |
| Seminal vesicles | Produce fluid that nourishes sperm and forms part of semen. |
| Prostate gland | Produces fluid that helps to protect and energize sperm. |
| Penis | Delivers sperm to the female reproductive tract. |
In males, ''spermatogenesis'' occurs in the testes, where sperm cells are produced. This process begins at puberty and continues throughout a man's life. Hormonal regulation is crucial, with testosterone being the primary male hormone influencing both the production of sperm and the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
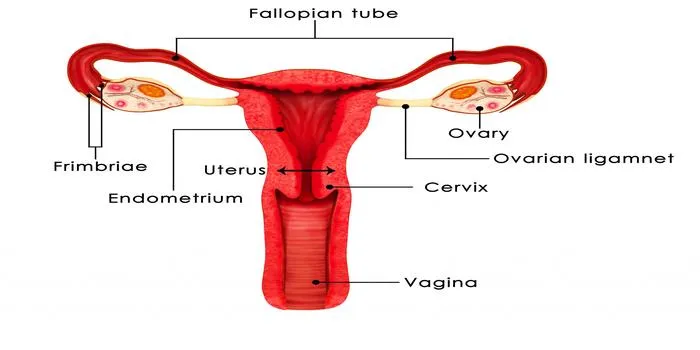
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system, located primarily in the pelvis, has its own set of organs with specific functions:
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Ovaries | Produce eggs (ova) and hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone. |
| Fallopian tubes | Transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus; site of fertilization. |
| Uterus | Houses and nourishes the developing fetus. |
| Cervix | Connects the uterus to the vagina; allows passage for sperm and menstrual fluids. |
| Vagina | Serves as the birth canal and the receptacle for the penis during intercourse. |
In females, ''oogenesis'' occurs in the ovaries, where eggs are produced. Unlike males, females are born with a finite number of eggs, and this number decreases with age. The ''menstrual cycle'' is a crucial aspect of female reproductive health, regulated by hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, preparing the body for potential pregnancy each month.
The Process of Fertilization
Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell successfully penetrates an egg, typically within the fallopian tube. This process marks the beginning of a new organism's development. Following fertilization, the zygote travels down the fallopian tube and into the uterus, where it can implant and develop into an embryo.
Importance of the Human Reproductive System
The ''human reproductive system'' plays a vital role in the continuation of the species. Understanding its anatomy and functions is essential for various reasons:
- ''Reproductive health'': Knowledge of the reproductive system helps individuals make informed decisions about their sexual health.
- ''Family planning'': Understanding fertility cycles can assist in planning or preventing pregnancy.
- ''Sex education'': Awareness of the reproductive system contributes to healthier relationships and responsible sexual behavior.
- ''Healthcare'': Recognizing symptoms of reproductive health issues can lead to early diagnosis and treatment.
Common Reproductive Health Issues
Both males and females can experience various reproductive health issues. Some common conditions include:
- ''Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)'': A hormonal disorder affecting women, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and fertility issues.
- ''Erectile Dysfunction'': A common issue in men, where they struggle to achieve or maintain an erection.
- ''Endometriosis'': A painful condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside it, affecting fertility and causing discomfort.
- ''Infertility'': Difficulty in conceiving due to various factors affecting either partner.
Conclusion
Understanding the ''human reproductive system'' is crucial for promoting reproductive health, making informed health choices, and addressing various conditions that can arise. By educating ourselves about this system, we can foster a healthier society that values reproductive health and well-being.