- Home >
- Health
- > Epidemiology
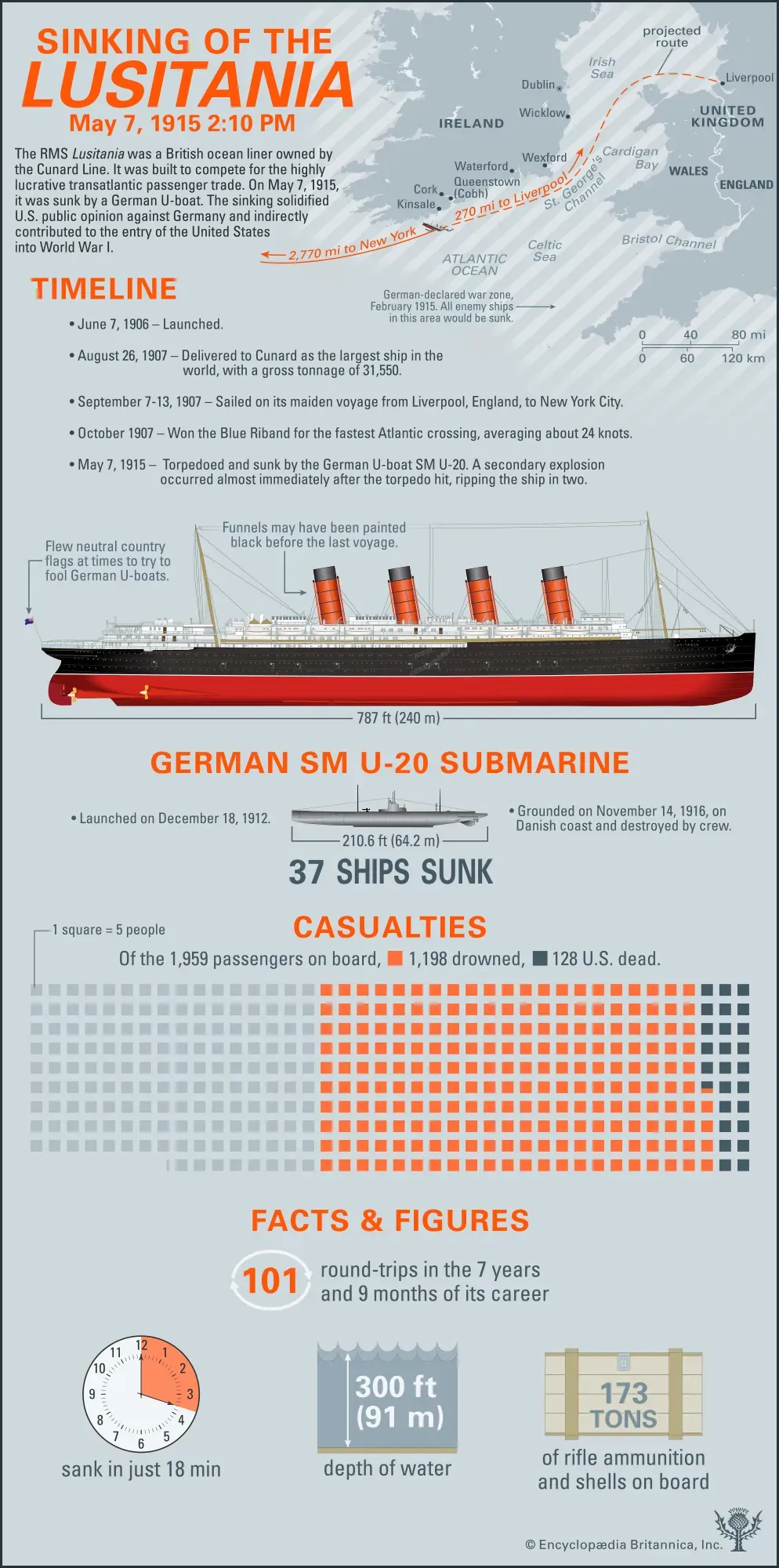
The Human Muscle System
"The Human Muscle System" delves into the intricate network of muscles that enable movement and support bodily functions, highlighting their roles in various physical activities. Meanwhile, "The Big Apple" explores the origins of New York City's nickname, often attributed to its vibrant cultural scene and significant contributions to music and arts. Additionally, the book examines the intriguing stories behind the nicknames of eight other famous cities, revealing how history, culture, and local characteristics shape their identities.
Advertisement
The Structure and Function of Muscles
The human muscle system is a complex network of tissues responsible for movement and stability in the body. It consists of over 600 muscles that work together to control both voluntary and involuntary actions. These muscles are categorized into three main types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Each type has a unique role in maintaining bodily functions, from enabling locomotion to facilitating digestion and circulation.
Skeletal muscles are attached to the bones by tendons and are under conscious control, allowing us to perform activities such as walking, running, and lifting. They are composed of elongated fibers and are characterized by a striated appearance due to the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments. These muscles play a vital role in maintaining posture and generating heat through contractions.
Smooth muscles, on the other hand, are found in the walls of hollow organs such as the intestines, blood vessels, and the bladder. Unlike skeletal muscles, they are not under voluntary control and help in processes like moving food through the digestive tract and regulating blood flow. Smooth muscles are spindle-shaped and lack the striated appearance of skeletal muscles.
Cardiac muscles are found only in the heart and are responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. They share characteristics with both skeletal and smooth muscles, being striated like skeletal muscles but involuntarily controlled like smooth muscles. The rhythmic contractions of cardiac muscles are essential for maintaining a consistent heartbeat.
The human muscle system works in conjunction with the nervous system to coordinate movement and respond to external stimuli. Muscles are stimulated by nerve impulses that trigger contractions, enabling a wide range of motions and activities. Proper muscle function is crucial not only for physical activity but also for overall health, as muscles contribute to metabolic processes, support the immune system, and protect vital organs. Regular exercise and proper nutrition are essential for maintaining muscle health and preventing conditions such as muscle atrophy and sarcopenia.