Just How Old Is
"Just How Old Is" explores the concept of age from various perspectives, delving into scientific, historical, and cultural aspects. It examines how age is perceived and measured, revealing intriguing insights into the aging process and its implications on society. The work also addresses the relativity of age in different contexts, such as technology and the universe. By combining empirical data with philosophical musings, it challenges conventional notions of time and encourages readers to rethink the significance of age.
When discussing the age of a person, event, or phenomenon, it often leads to intriguing questions and insights. The concept of age can be measured in various ways, and understanding it involves delving into historical contexts and cultural perceptions. In this article, we will explore the different aspects of age, how it is determined, and present relevant data in a structured format.
Understanding Age: A Multifaceted Concept
Age is not merely a number; it encompasses a range of interpretations. From biological age, which refers to the physical state of a body, to chronological age, which is the actual time elapsed since birth, age can be perceived through various lenses. This complexity is further amplified when discussing age in terms of cultural significance, societal expectations, and individual experiences.
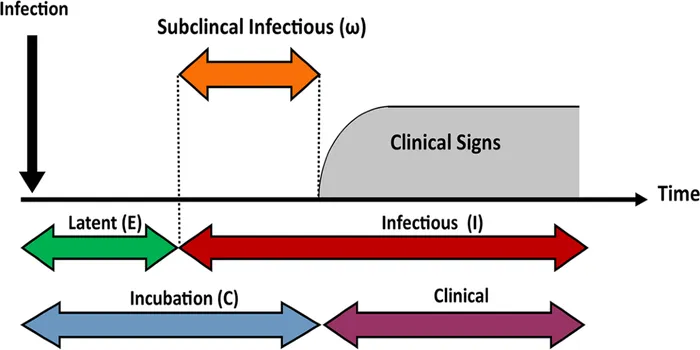
Chronological Age vs. Biological Age
Chronological age is the most straightforward definition, marking the time a person has been alive. In contrast, biological age takes into account the physical and functional state of an individual, which can differ significantly from chronological age. Factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and environment play crucial roles in determining biological age.
How Age Influences Perspectives
Age influences perspectives across many domains, including health, career, and social interactions. For instance, younger individuals may have different viewpoints on technology and innovation compared to older generations. Conversely, older individuals often bring valuable experience and knowledge to various discussions.
Age Across Cultures
Cultural interpretations of age can vary widely. In some societies, age is revered, and older individuals are seen as wise leaders. In contrast, other cultures may prioritize youth and innovation, often valuing the perspectives of younger generations more highly. Understanding these cultural nuances can provide deeper insights into global interactions and collaborations.
Data on Age Distribution
To better understand age demographics, let's explore some data representation through a table format. This data highlights the age distribution in various populations:
| Age Group | Percentage of Population |
|---|---|
| 0-14 years | 25% |
| 15-24 years | 15% |
| 25-54 years | 40% |
| 55-64 years | 10% |
| 65 years and older | 10% |
This table provides a clear snapshot of the age distribution in a given population, reflecting the demographic composition that can affect various sectors, including the workforce and consumer markets.
Significance of Age in Marketing
Understanding the age demographics of a target audience is crucial in marketing strategies. For businesses that leverage referrerAdCreative, age plays a significant role in tailoring advertisements to resonate with specific groups. For example, products aimed at younger audiences may utilize vibrant colors and dynamic content, while those targeting older demographics might focus on reliability and quality.
Age and Technology Adoption
The age of users significantly influences technology adoption rates. Younger generations are typically quicker to adopt new technologies, while older generations may take longer to acclimate. This trend highlights the importance of targeting advertisements effectively through referrerAdCreative strategies. Understanding the technological comfort levels of different age groups can help businesses tailor their marketing efforts to maximize engagement.
Age and Health Considerations
As individuals age, their health needs and concerns change. Younger adults may focus on fitness and wellness, while older adults often prioritize management of chronic conditions and preventive health measures. This shift necessitates different marketing approaches for health-related products and services, ensuring that messaging is appropriate for the audience's age group.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of Age
In conclusion, age is a multifaceted concept that extends beyond mere chronological measures. It encompasses biological, cultural, and social dimensions that significantly influence our perspectives and interactions. For businesses, understanding these nuances, especially in relation to referrerAdCreative, can provide insights into effective marketing strategies. By embracing the complexity of age, we can foster better communication and connections across generations, ultimately leading to a more cohesive society.
Whether considering individual experience or broader demographic trends, recognizing the significance of age can enhance our understanding of human behavior and societal dynamics.